Manufacturing Process of Cast Steel Parts

Steel Sand Casting
Steel sand casting uses sand as the casting material, then pours molten steel into the casting mold, takes out the casting after cooling, cleans and performs post-processing.
· The mold manufacturing cost is low and can be used many times
· Can cast large and medium-sized steel castings with complex shapes and large sizes.
· Suitable for small, medium and large batch production.

Steel Investment Casting
Steel investment casting uses soluble or combustible casting molds (such as wax molds) to make castings, and is often used to make steel parts with complex shapes and high precision requirements.
· High surface quality
· No need for a lot of post-processing
· Suitable for small batches and high precision steel parts

Steel Shell Mold Casting
Steel shell mold casting uses ceramics or other refractory materials as casting molds, and the casting mold is usually made by applying multiple layers of refractory coatings on the surface of the model.
· Suitable for small batches or high-value steel castings
· Used to produce small and medium-sized steel castings
· Make complex steel castings

Steel Lost Foam Casting
Steel lost foam casting uses a foam pattern to form the mold cavity. The pattern is coated with refractory material and surrounded by dry sand. When molten steel is poured into the mold, the foam pattern vaporizes and is replaced by the molten metal.
· High dimensional accuracy and good surface finish, reducing or eliminating the need for machining.
· Suitable for complex and thin-walled steel castings
· Applicable to small and medium batch production, material utilization.

Heat Treatment
Heat treatment is to change the internal structure and properties of steel materials by heating, insulation, cooling, etc., improve the mechanical properties of metals, extend service life, and optimize processing performance.
· Improve the hardness and strength of steel materials
· Improve the toughness of steel materials
· Improve wear resistance and corrosion resistance
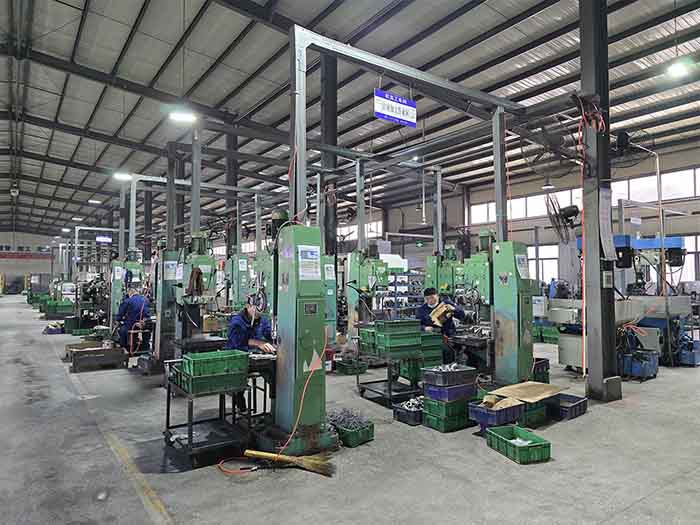

Machining
Mechanical machining is a post-processing process for castings. Through fine machining, the accuracy, surface quality and functionality of steel castings are improved.
· Optimize appearance quality
· Improve cast steel part structure and function
· Process thin walls and complex shapes
Different Materials of Steel Castings
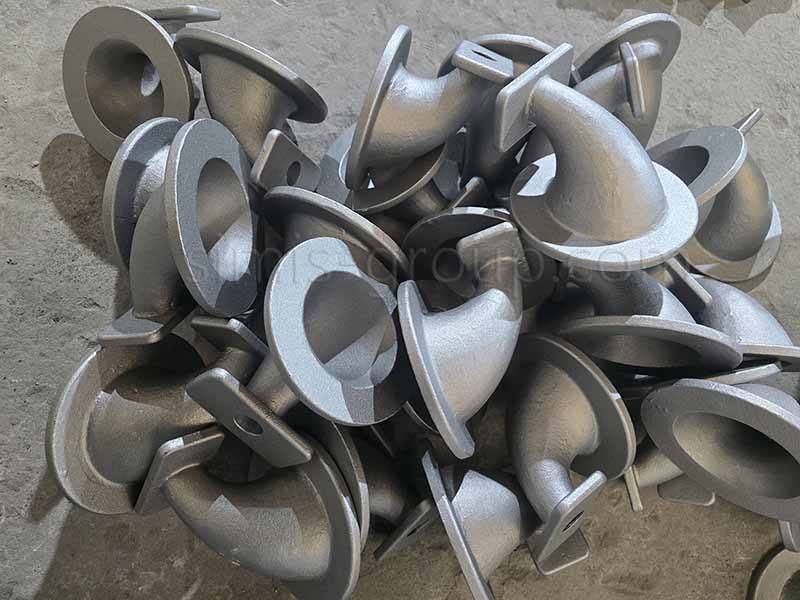
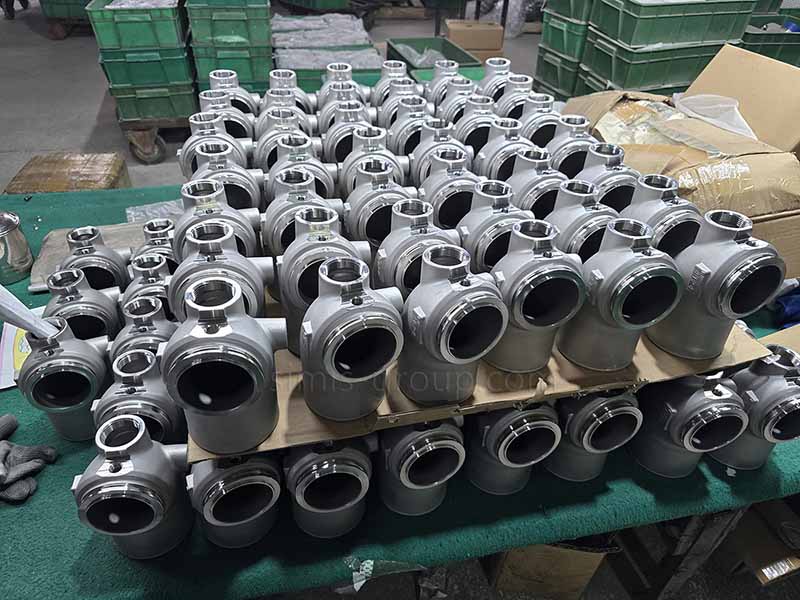
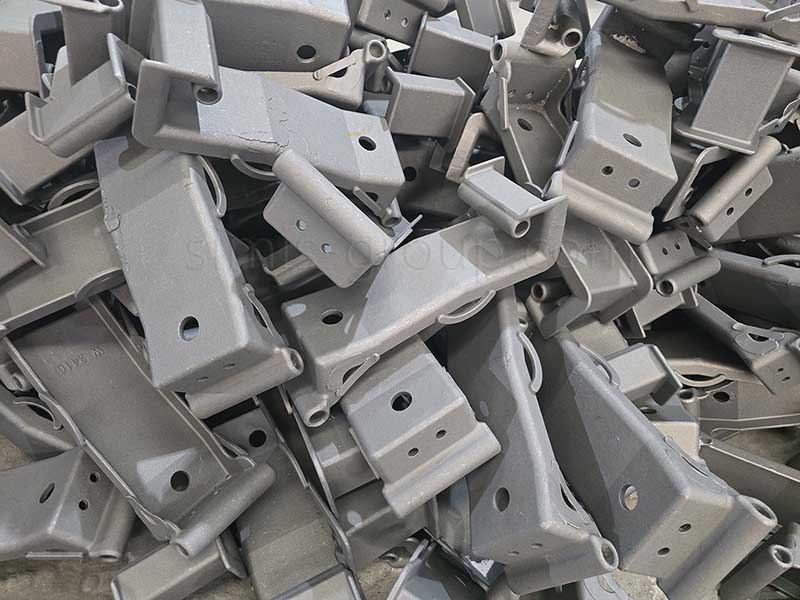



1. Carbon steel
Carbon steel casting is the direct production of steel castings through methods such as investment casting and shell casting. Carbon steel offers excellent casting properties, high strength, and excellent ductility and toughness. Cast carbon steel overcomes the shortcomings of cast iron in terms of ductility and toughness, offering excellent overall performance comparable to forged steel while maintaining the flexibility to form complex structures. It is suitable for manufacturing critical components with complex shapes and subject to heavy or impact loads.
· Excellent Castability: Moderate fluidity and high shrinkage (requiring appropriate riser and chill design) enable the production of complex castings.
· Excellent Overall Mechanical Properties: Combining high strength and hardness with ductility and impact toughness far exceeding that of cast iron, it can withstand impact and fatigue loads.
· Excellent Weldability: Medium and low carbon cast steels, in particular, exhibit excellent weldability, facilitating repair and assembly welding of castings.
· Heat Treatable: Heat treatment processes such as annealing, normalizing, and quenching and tempering can eliminate casting stresses, refine grains, and significantly improve mechanical properties.
Casting Carbon Steel Parts by Simis Steel Foundry:
Power plant equipment (valves, pump casings, turbine casings), mining machinery (track shoes, shovel teeth), heavy machinery (gears, mill frames, rollers), marine components (anchor chains, rudder stocks), and railway vehicles (couplers, bolsters, side frames).
Carbon Steel Casting Grades Used by Simis Steel Foundry:
· Low Carbon Cast Steel (Carbon content ≤ 0.25%)
Applications: Primarily used for manufacturing parts requiring high toughness and good weldability, such as engine bases, housings, marine components, and pressure vessels.
Common Grades: ASTM A216 Grade WCA; EN 10293 Grade GP240GH
· Medium Carbon Cast Steel (Carbon content 0.25% - 0.60%)
Applications: Used for manufacturing parts subject to heavy loads, fatigue loads, and certain impacts, such as gears, connecting rods, mill frames, and heavy-duty mill frames. Common grades: ASTM A216 Grade WCB, WCC; ASTM A27 Grade 70-40; EN 10293 Grade GP340GH
· High-carbon cast steel (Carbon content ≥ 0.60%)
Applications: Primarily used for manufacturing parts requiring high hardness and wear resistance, such as rolls, crusher jaws, and molds.
Common grades: ASTM A27 Grade 100-70
2. Alloy steel
Alloy steel casting involves adding significant amounts of alloying elements (such as nickel, chromium, molybdenum, and manganese) to carbon steel to enhance the mechanical properties, hardenability, and performance under severe service conditions. Compared to carbon steel, alloy steels offer greater strength, toughness, and wear resistance and can be tailored through heat treatment to specific applications such as high stress, wear, or high temperatures. The combination of specific alloying elements and customized heat treatment processes enables foundries to design materials with precise performance characteristics to meet the most demanding applications in the energy, mining, and heavy industries.
· Enhanced Mechanical Properties: The addition of alloying elements significantly increases tensile strength, yield strength, and impact toughness, especially in larger cross-sections.
· Excellent Hardenability: Alloying elements (particularly Cr, Mo, Ni) allow for deeper and more uniform hardening during heat treatment, enabling the production of high-strength heavy-section castings.
· Improved Wear and Abrasion Resistance: Certain compositions form hard carbides and microstructures that provide exceptional resistance to wear and abrasion.
· Good High-Temperature Performance: Retains strength and resists creep and thermal softening at elevated temperatures better than carbon steels.
· Good Low-Temperature Toughness: Nickel-alloyed grades maintain excellent impact resistance at sub-zero temperatures.
Alloy Steel Castings by Simis Steel Foundry:
Gears, pinions, and sprockets for heavy machinery; high-pressure valve bodies and pump casings for oil & gas; crusher liners, shovel teeth, and mining equipment components; turbine casings and power generation equipment; high-strength structural components for marine.
Alloy Steel Casting Grades Used by Simis Steel Foundry:
· High-Strength Low-Alloy (HSLA) Steels
Common Applications: Structural components, truck frames, crane booms, and mining equipment where weight reduction is important.
Common Grades: ASTM A148 Grade 80-50, 90-60, 105-85
· Heat-Treatable Alloy Steels (Cr-Mo / Ni-Cr-Mo)
Common Applications: Highly stressed components like gears, pinions, crankshafts, and pressure-containing parts for high-temperature service.
Common Grades: ASTM A217 Grade WC6 (1Cr-0.5Mo), WC9 (2.25Cr-1Mo); ASTM A487 Grade 4N (Ni-Cr-Mo)
· Wear-Resistant Alloy Steels
Common Applications: Crusher rolls, pulverizer hammers, grinding components, and material handling equipment.
Common Grades: ASTM A732 Grade A10 (0.5Cr-0.5Mo-1.0Ni), ASTM A128 Grade B-2 (12% Mn Steel - Austenitic)*
· Low-Temperature Nickel Alloy Steels
Common Applications: Components for liquefied gas storage and handling, and offshore structures.
Common Grades: ASTM A352 Grade LC2 (2.5% Ni), LC3 (3.5% Ni)
3. Stainless steel
Stainless steel offers excellent corrosion resistance, good high and low temperature mechanical properties, and exceptional castability, a unique combination of properties unmatched by carbon steel or low-alloy steel. Choosing the right stainless steel casting material depends on the specific application environment (corrosive media, temperature), required mechanical properties, and performance criteria. Stainless steel can be directly produced into corrosion- and heat-resistant components through investment casting, shell casting, and lost foam casting. It is an ideal choice for manufacturing critical components that must withstand harsh environments, high temperatures, or require high purity and complex geometries.
· Excellent Corrosion Resistance: The key feature of stainless steel, provided by a passive chromium-rich oxide layer, offers outstanding resistance to various corrosive media, including acids, alkalis, and chlorides.
· Good High-Temperature Performance: Suitable for continuous service in oxidizing or carburizing atmospheres at elevated temperatures, maintaining strength and resisting scaling.
· Good Low-Temperature Toughness: Certain grades retain excellent impact toughness and ductility at cryogenic temperatures, preventing brittle fracture.
· Hygienic and Easy to Clean: The non-porous, smooth surface of cast stainless steel is ideal for food, pharmaceutical, and chemical processing applications.
· Good Castability and Weldability: Most grades cast well, allowing for the production of complex shapes. They can also be readily repaired or fabricated using common welding techniques.
Stainless Steel Casting Grey iron parts by Simis Steel Foundry:
Valves, pumps, and fittings for chemical processing; impellers and turbine blades; food and beverage processing equipment; marine hardware and propeller components; medical and surgical instrument parts.
Stainless Steel Casting Grades Used by Simis Steel Foundry:
Stainless steel castings are primarily classified by their metallurgical structure, which determines their properties and applications.
· Austenitic Stainless Steels
Common Applications: Pump and valve bodies, chemical processing equipment, fittings for corrosive services, food processing parts.
Common Grades: ASTM A351 Grade CF8 (equivalent to 304), CF8M (equivalent to 316), CF3 (304L), CF3M (316L)
· Martensitic Stainless Steels
Common Applications: Pump shafts, valve trim, turbine parts, mechanical components requiring high strength and some corrosion resistance.
Common Grades: ASTM A217 Grade CA15, ASTM A743 Grade CA40
· Duplex (Austenitic-Ferritic) Stainless Steels
Common Applications: Pumps, valves, and fittings for offshore oil & gas, chemical tankers, and desalination plants.
Common Grades: ASTM A890 Grade 1B (CD3MN / equivalent to F51), Grade 4A (CE8MN / similar to F53)
· Ferritic Stainless Steels
Common Applications: Automotive exhaust components (manifolds, catalytic converter housings), heat exchangers for corrosive media, nitric acid production equipment, and applications requiring good resistance to chloride stress corrosion cracking.
Common Grades: ASTM A743 Grade CA27M (similar to wrought 430), ASTM A447 Grade G35 (high-chromium heat-resistant grade)
4. Tool steel
Tool steels are used to produce tool components that combine high hardness, wear resistance, and thermal stability. These steels are specially formulated to maintain a good cutting edge, resist deformation under load, and withstand abrasive wear at room and elevated temperatures. Cast tool steels are a cost-effective alternative to forged products. Tool geometries that would be difficult or expensive to achieve using forged bar stock are ideal. The casting process allows for the strategic placement of wear-resistant material in the mold and the integration of conformal cooling channels, making them suitable for manufacturing complex-shaped tools, molds, and wear parts.
· High Hardness and Wear Resistance: Achieve and maintain very high surface hardness (up to 60+ HRC) through heat treatment, providing exceptional resistance to abrasive and adhesive wear.
· Good Dimensional Stability: Exhibit minimal size change during heat treatment, crucial for precision tools and dies.
· High Resistance to Softening (Red Hardness): Certain grades retain their hardness and strength at elevated temperatures (up to 500-600°C), which is essential for hot-working applications.
· Adequate Toughness: Possess sufficient toughness to withstand impact and shock loading without chipping or fracturing.
· Good Machinability (in annealed state): Can be machined to precise dimensions in their soft, annealed condition prior to final hardening.
Tool Steel Castings by Simis Steel Foundry:
Die casting dies and cores; forging dies and punches; plastic injection molds; cutting tools and blades; wear plates and liners; cold-work punches and trimming dies; hot-work extrusion dies.
Tool Steel Casting Grades Used by Simis Steel Foundry:
· Cold-Work Tool Steels
Common Applications: Blanking and punching dies, shearing blades, thread rolling dies, slitting cutters, and precision gauges.
Common Grades: ASTM A597 Grade CA-2 (similar to AISI A2 air-hardening), ASTM A597 Grade CD-2 (similar to AISI D2 high-carbon-high-chromium)
· Hot-Work Tool Steels
Common Applications: Die casting dies, extrusion dies, forging dies, hot punches, and mandrels.
Common Grades: ASTM A597 Grade HA-1 (similar to AISI H13 chromium hot-work steel), ASTM A597 Grade HB-2 (similar to AISI H21 tungsten hot-work steel)
· Plastic Mold Steels
Common Applications: Injection mold cavities and cores, compression molds, mold bases, and ejector pins.
Common Grades: ASTM A597 Grade P-2 (similar to AISI P20 low-carbon chromium-molybdenum), ASTM A597 Grade P-4 (similar to AISI P4 nickel-chromium)
· High-Speed Tool Steels
Common Applications: Complex cutting tools, drill bits, milling cutters, and saw blades produced via casting for near-net-shape efficiency.
Common Grades: ASTM A597 Grade M-2 (Molybdenum-type high-speed steel), ASTM A597 Grade M-4 (Higher vanadium/carbon Moly-type)
1. Carbon steel
Carbon steel casting is the direct production of steel castings through methods such as investment casting and shell casting. Carbon steel offers excellent casting properties, high strength, and excellent ductility and toughness. Cast carbon steel overcomes the shortcomings of cast iron in terms of ductility and toughness, offering excellent overall performance comparable to forged steel while maintaining the flexibility to form complex structures. It is suitable for manufacturing critical components with complex shapes and subject to heavy or impact loads.
· Excellent Castability: Moderate fluidity and high shrinkage (requiring appropriate riser and chill design) enable the production of complex castings.
· Excellent Overall Mechanical Properties: Combining high strength and hardness with ductility and impact toughness far exceeding that of cast iron, it can withstand impact and fatigue loads.
· Excellent Weldability: Medium and low carbon cast steels, in particular, exhibit excellent weldability, facilitating repair and assembly welding of castings.
· Heat Treatable: Heat treatment processes such as annealing, normalizing, and quenching and tempering can eliminate casting stresses, refine grains, and significantly improve mechanical properties.
Casting Carbon Steel Parts by Simis Steel Foundry:
Power plant equipment (valves, pump casings, turbine casings), mining machinery (track shoes, shovel teeth), heavy machinery (gears, mill frames, rollers), marine components (anchor chains, rudder stocks), and railway vehicles (couplers, bolsters, side frames).
Carbon Steel Casting Grades Used by Simis Steel Foundry:
· Low Carbon Cast Steel (Carbon content ≤ 0.25%)
Applications: Primarily used for manufacturing parts requiring high toughness and good weldability, such as engine bases, housings, marine components, and pressure vessels.
Common Grades: ASTM A216 Grade WCA; EN 10293 Grade GP240GH
· Medium Carbon Cast Steel (Carbon content 0.25% - 0.60%)
Applications: Used for manufacturing parts subject to heavy loads, fatigue loads, and certain impacts, such as gears, connecting rods, mill frames, and heavy-duty mill frames. Common grades: ASTM A216 Grade WCB, WCC; ASTM A27 Grade 70-40; EN 10293 Grade GP340GH
· High-carbon cast steel (Carbon content ≥ 0.60%)
Applications: Primarily used for manufacturing parts requiring high hardness and wear resistance, such as rolls, crusher jaws, and molds.
Common grades: ASTM A27 Grade 100-70
2. Alloy steel
Alloy steel casting involves adding significant amounts of alloying elements (such as nickel, chromium, molybdenum, and manganese) to carbon steel to enhance the mechanical properties, hardenability, and performance under severe service conditions. Compared to carbon steel, alloy steels offer greater strength, toughness, and wear resistance and can be tailored through heat treatment to specific applications such as high stress, wear, or high temperatures. The combination of specific alloying elements and customized heat treatment processes enables foundries to design materials with precise performance characteristics to meet the most demanding applications in the energy, mining, and heavy industries.
· Enhanced Mechanical Properties: The addition of alloying elements significantly increases tensile strength, yield strength, and impact toughness, especially in larger cross-sections.
· Excellent Hardenability: Alloying elements (particularly Cr, Mo, Ni) allow for deeper and more uniform hardening during heat treatment, enabling the production of high-strength heavy-section castings.
· Improved Wear and Abrasion Resistance: Certain compositions form hard carbides and microstructures that provide exceptional resistance to wear and abrasion.
· Good High-Temperature Performance: Retains strength and resists creep and thermal softening at elevated temperatures better than carbon steels.
· Good Low-Temperature Toughness: Nickel-alloyed grades maintain excellent impact resistance at sub-zero temperatures.
Alloy Steel Castings by Simis Steel Foundry:
Gears, pinions, and sprockets for heavy machinery; high-pressure valve bodies and pump casings for oil & gas; crusher liners, shovel teeth, and mining equipment components; turbine casings and power generation equipment; high-strength structural components for marine.
Alloy Steel Casting Grades Used by Simis Steel Foundry:
· High-Strength Low-Alloy (HSLA) Steels
Common Applications: Structural components, truck frames, crane booms, and mining equipment where weight reduction is important.
Common Grades: ASTM A148 Grade 80-50, 90-60, 105-85
· Heat-Treatable Alloy Steels (Cr-Mo / Ni-Cr-Mo)
Common Applications: Highly stressed components like gears, pinions, crankshafts, and pressure-containing parts for high-temperature service.
Common Grades: ASTM A217 Grade WC6 (1Cr-0.5Mo), WC9 (2.25Cr-1Mo); ASTM A487 Grade 4N (Ni-Cr-Mo)
· Wear-Resistant Alloy Steels
Common Applications: Crusher rolls, pulverizer hammers, grinding components, and material handling equipment.
Common Grades: ASTM A732 Grade A10 (0.5Cr-0.5Mo-1.0Ni), ASTM A128 Grade B-2 (12% Mn Steel - Austenitic)*
· Low-Temperature Nickel Alloy Steels
Common Applications: Components for liquefied gas storage and handling, and offshore structures.
Common Grades: ASTM A352 Grade LC2 (2.5% Ni), LC3 (3.5% Ni)
3. Stainless steel
Stainless steel offers excellent corrosion resistance, good high and low temperature mechanical properties, and exceptional castability, a unique combination of properties unmatched by carbon steel or low-alloy steel. Choosing the right stainless steel casting material depends on the specific application environment (corrosive media, temperature), required mechanical properties, and performance criteria. Stainless steel can be directly produced into corrosion- and heat-resistant components through investment casting, shell casting, and lost foam casting. It is an ideal choice for manufacturing critical components that must withstand harsh environments, high temperatures, or require high purity and complex geometries.
· Excellent Corrosion Resistance: The key feature of stainless steel, provided by a passive chromium-rich oxide layer, offers outstanding resistance to various corrosive media, including acids, alkalis, and chlorides.
· Good High-Temperature Performance: Suitable for continuous service in oxidizing or carburizing atmospheres at elevated temperatures, maintaining strength and resisting scaling.
· Good Low-Temperature Toughness: Certain grades retain excellent impact toughness and ductility at cryogenic temperatures, preventing brittle fracture.
· Hygienic and Easy to Clean: The non-porous, smooth surface of cast stainless steel is ideal for food, pharmaceutical, and chemical processing applications.
· Good Castability and Weldability: Most grades cast well, allowing for the production of complex shapes. They can also be readily repaired or fabricated using common welding techniques.
Stainless Steel Casting Grey iron parts by Simis Steel Foundry:
Valves, pumps, and fittings for chemical processing; impellers and turbine blades; food and beverage processing equipment; marine hardware and propeller components; medical and surgical instrument parts.
Stainless Steel Casting Grades Used by Simis Steel Foundry:
Stainless steel castings are primarily classified by their metallurgical structure, which determines their properties and applications.
· Austenitic Stainless Steels
Common Applications: Pump and valve bodies, chemical processing equipment, fittings for corrosive services, food processing parts.
Common Grades: ASTM A351 Grade CF8 (equivalent to 304), CF8M (equivalent to 316), CF3 (304L), CF3M (316L)
· Martensitic Stainless Steels
Common Applications: Pump shafts, valve trim, turbine parts, mechanical components requiring high strength and some corrosion resistance.
Common Grades: ASTM A217 Grade CA15, ASTM A743 Grade CA40
· Duplex (Austenitic-Ferritic) Stainless Steels
Common Applications: Pumps, valves, and fittings for offshore oil & gas, chemical tankers, and desalination plants.
Common Grades: ASTM A890 Grade 1B (CD3MN / equivalent to F51), Grade 4A (CE8MN / similar to F53)
· Ferritic Stainless Steels
Common Applications: Automotive exhaust components (manifolds, catalytic converter housings), heat exchangers for corrosive media, nitric acid production equipment, and applications requiring good resistance to chloride stress corrosion cracking.
Common Grades: ASTM A743 Grade CA27M (similar to wrought 430), ASTM A447 Grade G35 (high-chromium heat-resistant grade)
4. Tool steel
Tool steels are used to produce tool components that combine high hardness, wear resistance, and thermal stability. These steels are specially formulated to maintain a good cutting edge, resist deformation under load, and withstand abrasive wear at room and elevated temperatures. Cast tool steels are a cost-effective alternative to forged products. Tool geometries that would be difficult or expensive to achieve using forged bar stock are ideal. The casting process allows for the strategic placement of wear-resistant material in the mold and the integration of conformal cooling channels, making them suitable for manufacturing complex-shaped tools, molds, and wear parts.
· High Hardness and Wear Resistance: Achieve and maintain very high surface hardness (up to 60+ HRC) through heat treatment, providing exceptional resistance to abrasive and adhesive wear.
· Good Dimensional Stability: Exhibit minimal size change during heat treatment, crucial for precision tools and dies.
· High Resistance to Softening (Red Hardness): Certain grades retain their hardness and strength at elevated temperatures (up to 500-600°C), which is essential for hot-working applications.
· Adequate Toughness: Possess sufficient toughness to withstand impact and shock loading without chipping or fracturing.
· Good Machinability (in annealed state): Can be machined to precise dimensions in their soft, annealed condition prior to final hardening.
Tool Steel Castings by Simis Steel Foundry:
Die casting dies and cores; forging dies and punches; plastic injection molds; cutting tools and blades; wear plates and liners; cold-work punches and trimming dies; hot-work extrusion dies.
Tool Steel Casting Grades Used by Simis Steel Foundry:
· Cold-Work Tool Steels
Common Applications: Blanking and punching dies, shearing blades, thread rolling dies, slitting cutters, and precision gauges.
Common Grades: ASTM A597 Grade CA-2 (similar to AISI A2 air-hardening), ASTM A597 Grade CD-2 (similar to AISI D2 high-carbon-high-chromium)
· Hot-Work Tool Steels
Common Applications: Die casting dies, extrusion dies, forging dies, hot punches, and mandrels.
Common Grades: ASTM A597 Grade HA-1 (similar to AISI H13 chromium hot-work steel), ASTM A597 Grade HB-2 (similar to AISI H21 tungsten hot-work steel)
· Plastic Mold Steels
Common Applications: Injection mold cavities and cores, compression molds, mold bases, and ejector pins.
Common Grades: ASTM A597 Grade P-2 (similar to AISI P20 low-carbon chromium-molybdenum), ASTM A597 Grade P-4 (similar to AISI P4 nickel-chromium)
· High-Speed Tool Steels
Common Applications: Complex cutting tools, drill bits, milling cutters, and saw blades produced via casting for near-net-shape efficiency.
Common Grades: ASTM A597 Grade M-2 (Molybdenum-type high-speed steel), ASTM A597 Grade M-4 (Higher vanadium/carbon Moly-type)
Application of Steel Castings
Custom Steel Castings by Simis Steel Foundry
Steel Castings Company's Custom Steps


Confirm customization requirements
1. Provide detailed design documents or samples of parts
The engineering team will review the 3D drawings (CAD models) and corresponding processing plans provided by customers to ensure that they meet manufacturing requirements.
Samples: If customers provide samples, we can also produce according to samples.
2. Confirm the material of the steel casting
Choose the appropriate cast steel material according to the use environment, technical requirements or customer requirements of the parts. We will give reasonable suggestions based on the price, mechanical properties, wear resistance, corrosion resistance, etc. of the materials.
3. Confirm the casting process
Determine the appropriate steel casting process based on customer needs and part price, shape, size, precision, material, etc.
4. Confirm the requirements for various product attributes
Confirm the various performance requirements of the parts under the casting process and materials, such as strength, hardness, wear resistance, corrosion resistance, etc.
According to the drawings and product requirements, confirm the dimensional tolerance and precision requirements, surface roughness, appearance quality and other requirements of the product.
5. Make molds and samples
Make casting molds that meet the requirements according to the drawings or samples provided by the customer; and cast the selected casting materials through the corresponding process to produce the first batch of samples
6. Comprehensive inspection of samples
The produced steel casting samples will be fully inspected, including size and tolerance inspection, performance test, chemical composition analysis, non-destructive testing and other test reports.
7. Mass production
After the samples are confirmed and approved by the customer, arrange the mass production plan according to the order requirements and prepare the production materials.
Production and quality control
8. Quality control in mass production
We implement strict quality control measures during the production process to ensure that the quality of each steel casting in mass production meets customer requirements.
Production process quality monitoring: Regular sampling during the production process to check the size, appearance, physical properties, etc. of steel castings to ensure the consistency of each batch of parts.
Equipment inspection: Regularly inspect production equipment to avoid production deviations due to equipment failure.
9. Product quality inspection after production
Multiple inspections by multiple people: We will arrange different inspectors to conduct multiple random inspections on the final product, including dimensional accuracy, surface quality, strength, hardness, etc., to ensure that the parts produced meet customer requirements.
Quality inspection report: Provide a detailed quality inspection report for each steel casting inspected.
10. Parts packaging and delivery
Packaging: For parts that pass the quality inspection, pack and ship them, choose the appropriate packaging method and the appropriate logistics method (such as air, sea, and land transportation) to avoid damage during transportation and deliver them to customers on time.




If you want to custom parts, please send me the design drawings and 3D drawings of theparts you want to customize by email, and we will calculate an accurate price for you bylooking at the detailed part parameters and 3D model.























































