Custom Metal Parts For Energy Power Equipment
Customized casting and forging parts can be used in the energy and power equipment industry in the fields of power generation, transmission and distribution, energy storage, structural support, energy mining, renewable energy and marine energy equipment. They are the key support for the efficient, safe and stable operation of equipment. The high strength, corrosion resistance, high temperature resistance and high precision of customized parts enable the parts to adapt to extreme working conditions, extend equipment life and reduce maintenance costs.
Energy Power Equipment Parts Classification
1. Power generation equipment components
Castings and forgings are indispensable core components in power generation equipment such as thermal power, hydropower, wind power and nuclear power, such as turbine housings, turbine main shafts, blade roots, etc. They have high strength, high temperature resistance and fatigue resistance, can operate stably under high pressure, high speed and complex dynamic load conditions, and provide reliable support for the efficient energy conversion of equipment.
· Castings: turbine housing, guide vane housing, wind turbine hub, base
· Forgings: steam turbine main shaft, rotor, blade root
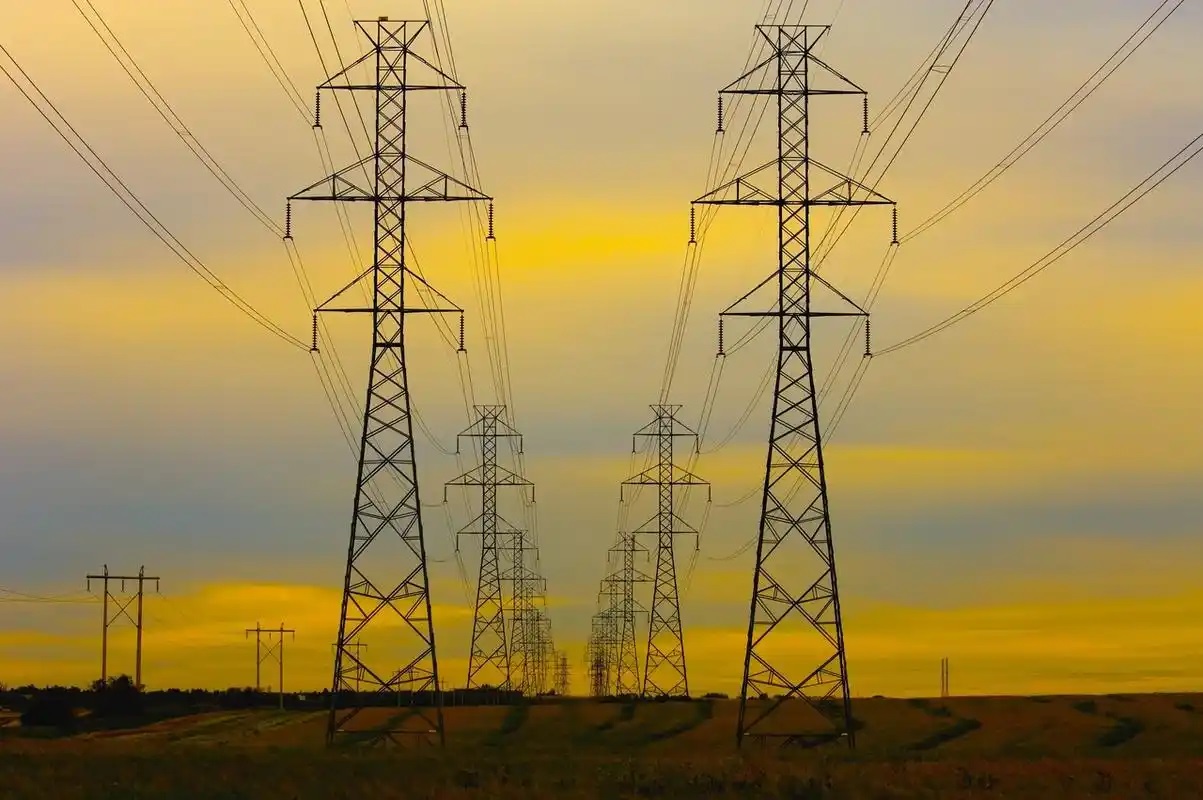

2. Power transmission and distribution equipment components
Castings and forgings in power transmission and distribution equipment, including transformer housings, conductive joints, terminals and support frames, are responsible for protection, conduction and support. Their excellent conductivity, corrosion resistance and structural stability ensure the efficient transmission of electricity and the long-term operation of equipment.
· Castings: transformer housing, transformer oil tank, cable junction box
· Forgings: high-voltage conductor connectors, terminals, insulator supports
3. Energy storage equipment components
In battery energy storage and mechanical energy storage equipment, castings and forgings are used to manufacture key components such as housings, heat sinks, sealing valve seats and support frames. With excellent sealing, corrosion resistance and high strength performance, they ensure the thermal management and mechanical stability of energy storage equipment.
· Castings: energy storage equipment housing, heat sink, sealing valve seat
· Forgings: high-strength connectors, support frames
4. Structural support components
Large energy equipment requires strong structural support. Castings and forgings such as equipment bases, flanges, support shafts, etc. provide high rigidity and durability for the equipment. They perform well under heavy loads and complex environments, ensuring the stability and precision of the equipment.
· Castings: equipment supports, bases, tower flanges
· Forgings: support shafts, couplings, bolts, nuts
5. Energy extraction equipment components
Castings and forgings in energy extraction equipment such as oil, natural gas and geothermal, such as wellhead device housings, drill pipe joints, pump bodies and high-pressure seals, need to withstand extreme pressure, corrosion and high temperature environments. Their excellent strength and durability provide long-term support for the energy extraction process.
· Castings: wellhead housing, pump housing, mud pump cylinder sleeve
· Forgings: drill pipe joints, valve bodies, high-pressure seals
6. Renewable energy equipment components
In wind, solar and marine energy equipment, castings and forgings are used to manufacture components such as wind turbine hubs, tower foundations, photovoltaic brackets and marine energy device main shafts. They have anti-fatigue, high strength and corrosion resistance, adapt to changing natural working conditions, and lay the foundation for the efficient use and large-scale application of renewable energy.
· Castings: wind turbine hub, tower foundation, photovoltaic bracket connector, tracking system base
· Forgings: wind turbine shaft, ocean energy device main shaft, turbine blade root
7. Marine energy and offshore equipment components
Castings and forgings play a vital role in marine energy and offshore equipment, and are widely used in marine energy power generation devices, offshore oil drilling platforms, floating production storage and offloading devices (FPSO) and submarine pipeline systems. Key components include the main shaft of wave energy conversion devices, offshore wind power foundation piles, platform support structures and pipeline joints. Castings and forgings are resistant to seawater corrosion, high strength and fatigue resistance, and can cope with harsh marine environments and complex dynamic loads.
· Castings: platform support feet, mud pump housings, pipe fixing brackets, equipment housings
· Forgings: lifting hooks, mooring chain links, high-pressure valve bodies, fasteners, connecting flanges
Available Materials For Energy Power Equipment Parts
Cast iron
In the petroleum, energy, and power generation industries, cast iron is processed into various parts through sand casting, lost foam casting, and heat treatment.
·Gray cast iron
Gray cast iron has excellent vibration absorption properties and is used in pump bodies, valve bodies, and gearbox housings after casting, reducing vibration and ensuring operational stability.
·Ductile iron
Ductile iron has high strength and excellent toughness. Sand or lost foam casting makes it suitable for rotors, pump casings, compressor parts, and bearing seats, capable of withstanding shock and high loads.
·Compacted graphite iron
Compacted graphite iron combines vibration absorption and strength. After casting, it is used in large chassis components, brackets, and long-term load-bearing structural parts.
·Alloy cast iron
Alloy cast iron is wear-resistant and heat-resistant. Through temperature-controlled casting or alloying, it is used in pump impellers, valve discs, wear parts, and parts used in high-temperature environments. Some parts can be enhanced with localized heat treatment or finishing.
Steel
In petroleum, energy, and power generation equipment, steel is used to manufacture various load-bearing and wear-resistant parts through forging, casting, heat treatment, and precision machining.
·Carbon steel
Carbon steel offers high strength and toughness, and can be forged, cast, or machined into parts such as pump shafts, drive shafts, connecting rods, gears, and hydraulic rods, used in applications subject to high torque and shock loads.
·Low-alloy steel
Low-alloy steel offers excellent wear and fatigue resistance, making it suitable for forging or casting hydraulic pump housings, valve bodies, high-stress connectors, and brackets, ensuring long-term, stable operation.
·Cast steel
Cast steel offers excellent formability, and can be fabricated through sand molding or precision casting into large structural components such as pump bodies, turbine housings, generator bases, and compressor housings, ensuring dimensional accuracy and mechanical properties.
·High-manganese steel
High-manganese steel offers wear and impact resistance, and can be cast and heat-treated to manufacture coal mill liners, conveyor rollers, crusher rollers, and pump impellers, suitable for high-load and shock conditions.
·Stainless steel
Stainless steel has excellent corrosion resistance and chemical resistance. It can be made into pump bodies, valve bodies, pipe joints and fasteners through casting or machining. It is stable for long-term use in humid, chemical-containing or corrosive environments.
Aluminum Alloy
Aluminum alloys are used in oil, energy, and power generation equipment to create lightweight, corrosion-resistant parts through die casting, gravity casting, extrusion, and machining.
·High-strength aluminum alloys
High-strength aluminum alloys, with their light weight and high specific strength, are used in instrument housings, control panel brackets, and lightweight structural components through die casting or extrusion, reducing equipment weight while maintaining strength.
·Corrosion-resistant aluminum alloys
Corrosion-resistant aluminum alloys, which can form a dense oxide film on their surfaces, are used in pump guides, valve plates, and fasteners through precision casting or machining, enhancing durability.
·Easy-to-machine aluminum alloys
Easy-to-machine aluminum alloys are easy to machine and weld, making them suitable for complex shapes such as end caps, shrouds, and electrical boxes. Heat treatment can optimize strength and toughness.
Other Metal Alloys
In addition to cast iron, steel, and aluminum, the oil, energy, and power generation industries utilize specialty metals to withstand high temperatures, high pressures, corrosion, and wear.
·Copper and copper alloys
They offer excellent electrical conductivity and wear resistance and are used in pump shaft bushings, valve seats, electrical conductors, and contactors through casting or machining.
·Titanium alloys
They offer high strength and corrosion resistance and are suitable for forging or machining into pump blades, fasteners, and high-temperature pipe supports.
·Magnesium alloys
They offer low density and excellent machinability and are used in instrument housings, lightweight brackets, and non-load-bearing structural components through die-casting and machining to reduce overall weight.
·Molybdenum and molybdenum alloys
They offer high-temperature and wear resistance and are used in high-temperature furnace components, brake components, bearing seats, and pump impellers through casting or forging.
Cast iron
In the petroleum, energy, and power generation industries, cast iron is processed into various parts through sand casting, lost foam casting, and heat treatment.
·Gray cast iron
Gray cast iron has excellent vibration absorption properties and is used in pump bodies, valve bodies, and gearbox housings after casting, reducing vibration and ensuring operational stability.
·Ductile iron
Ductile iron has high strength and excellent toughness. Sand or lost foam casting makes it suitable for rotors, pump casings, compressor parts, and bearing seats, capable of withstanding shock and high loads.
·Compacted graphite iron
Compacted graphite iron combines vibration absorption and strength. After casting, it is used in large chassis components, brackets, and long-term load-bearing structural parts.
·Alloy cast iron
Alloy cast iron is wear-resistant and heat-resistant. Through temperature-controlled casting or alloying, it is used in pump impellers, valve discs, wear parts, and parts used in high-temperature environments. Some parts can be enhanced with localized heat treatment or finishing.
Steel
In petroleum, energy, and power generation equipment, steel is used to manufacture various load-bearing and wear-resistant parts through forging, casting, heat treatment, and precision machining.
·Carbon steel
Carbon steel offers high strength and toughness, and can be forged, cast, or machined into parts such as pump shafts, drive shafts, connecting rods, gears, and hydraulic rods, used in applications subject to high torque and shock loads.
·Low-alloy steel
Low-alloy steel offers excellent wear and fatigue resistance, making it suitable for forging or casting hydraulic pump housings, valve bodies, high-stress connectors, and brackets, ensuring long-term, stable operation.
·Cast steel
Cast steel offers excellent formability, and can be fabricated through sand molding or precision casting into large structural components such as pump bodies, turbine housings, generator bases, and compressor housings, ensuring dimensional accuracy and mechanical properties.
·High-manganese steel
High-manganese steel offers wear and impact resistance, and can be cast and heat-treated to manufacture coal mill liners, conveyor rollers, crusher rollers, and pump impellers, suitable for high-load and shock conditions.
·Stainless steel
Stainless steel has excellent corrosion resistance and chemical resistance. It can be made into pump bodies, valve bodies, pipe joints and fasteners through casting or machining. It is stable for long-term use in humid, chemical-containing or corrosive environments.
Aluminum Alloy
Aluminum alloys are used in oil, energy, and power generation equipment to create lightweight, corrosion-resistant parts through die casting, gravity casting, extrusion, and machining.
·High-strength aluminum alloys
High-strength aluminum alloys, with their light weight and high specific strength, are used in instrument housings, control panel brackets, and lightweight structural components through die casting or extrusion, reducing equipment weight while maintaining strength.
·Corrosion-resistant aluminum alloys
Corrosion-resistant aluminum alloys, which can form a dense oxide film on their surfaces, are used in pump guides, valve plates, and fasteners through precision casting or machining, enhancing durability.
·Easy-to-machine aluminum alloys
Easy-to-machine aluminum alloys are easy to machine and weld, making them suitable for complex shapes such as end caps, shrouds, and electrical boxes. Heat treatment can optimize strength and toughness.
Other Metal Alloys
In addition to cast iron, steel, and aluminum, the oil, energy, and power generation industries utilize specialty metals to withstand high temperatures, high pressures, corrosion, and wear.
·Copper and copper alloys
They offer excellent electrical conductivity and wear resistance and are used in pump shaft bushings, valve seats, electrical conductors, and contactors through casting or machining.
·Titanium alloys
They offer high strength and corrosion resistance and are suitable for forging or machining into pump blades, fasteners, and high-temperature pipe supports.
·Magnesium alloys
They offer low density and excellent machinability and are used in instrument housings, lightweight brackets, and non-load-bearing structural components through die-casting and machining to reduce overall weight.
·Molybdenum and molybdenum alloys
They offer high-temperature and wear resistance and are used in high-temperature furnace components, brake components, bearing seats, and pump impellers through casting or forging.
How To Customize Energy Power Equipment Parts
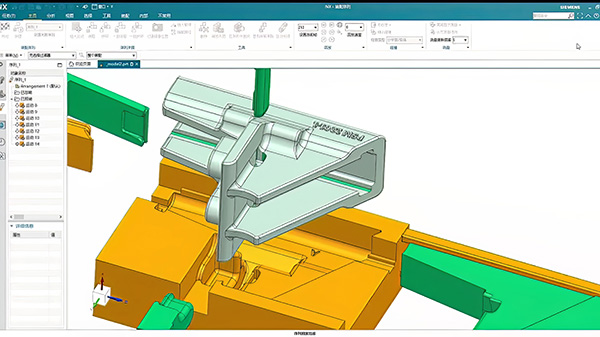
3D Drawings
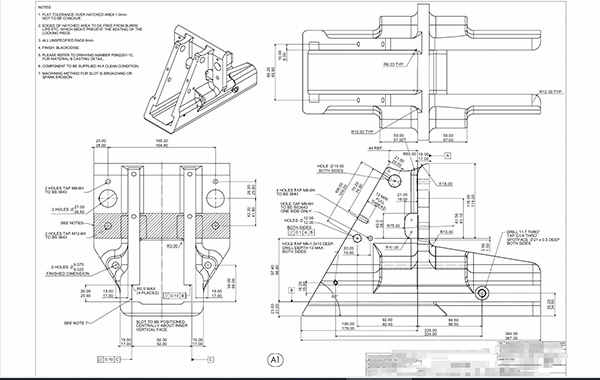
Processing Drawings

Sample
1. Provide Detailed Design Documents Or Samples
2. Confirm Material/Process/Performance
3. Make Molds And Samples
4. Comprehensive Sample Inspection
5. Mass Production
6. Post-production Parts Multiple Quality Inspections
1. Provide Detailed Design Documents Or Samples
2. Confirm Material/Process/Performance
3. Make Molds And Samples
4. Comprehensive Sample Inspection
5. Mass Production
6. Post-production Parts Multiple Quality Inspections
Custom Processing of Energy Power Equipment Parts

Casting
In the energy and power equipment industry, casting is used to produce large and complex parts in power generation systems such as turbine housings, generator housings and pump bodies, enabling customized parts to have high strength, wear resistance and the ability to withstand the high pressures and temperatures common in energy and power applications.

Forging
In the field of energy and power equipment, forging processes mainly produce components such as turbine blades, shafts and valve bodies. These forgings have excellent fatigue resistance, high strength and toughness, enabling the parts to operate reliably for a long time in high-stress environments such as power plants.
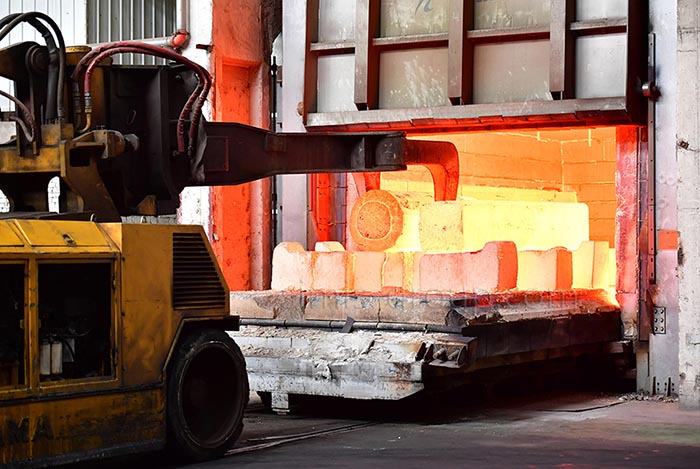

Heat Treatment
In the energy and power equipment industry, heat treatment processes are used to improve the performance of components such as turbine blades, pressure vessels and pump components. By improving properties such as wear resistance and fatigue strength, these components can withstand the high temperatures, high pressures and continuous operation common in power generation equipment, thereby increasing product service life and reliability.
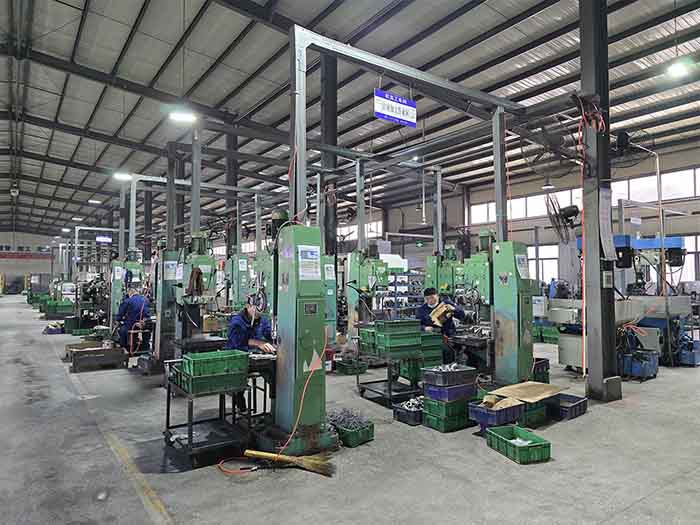

Machining
In the energy and power equipment sector, machining is used to produce high-precision components such as turbine shafts, pump impellers and generator rotors. Machining ensures that components meet tight tolerances and fit correctly into complex assemblies, allowing machines to run smoothly and efficiently with minimal friction and maximum reliability in demanding power generation systems.

Sheet Metal Fabrication
In energy and power equipment manufacturing, sheet metal fabrication is used to produce structural components such as heat exchangers, housings, and supports for generators and turbines, which assemble power generation systems and ensure reliable operation of the equipment under mechanical stress and environmental conditions.

Surface Treatment
In the energy and power equipment industry, surface treatment is applied to components such as turbine blades, pressure vessels and heat exchangers to protect them from environmental damage, including corrosion and erosion. Surface treatment processes can increase the service life of key components, reduce maintenance costs, and improve the overall efficiency and reliability of power generation equipment.



































