Custom Metal Parts For Trucks & Automotive
Metal parts for trucks and cars are often manufactured using materials such as steel, aluminum alloys, and cast iron to meet specific requirements such as high strength, lightweight design, corrosion resistance, and heat resistance. Custom truck and car metal parts include engine parts (e.g., pistons, crankshafts), suspension systems (e.g., control arms, shock absorbers), structural elements (e.g., chassis, frame brackets), and critical transmission components (e.g., gears, shafts). Custom manufacturing processes such as casting, forging, and machining enable precise specifications, ensuring that parts can withstand the harsh operating conditions of trucks and cars, including heavy loads, high speeds, and various environmental factors. Customization can improve vehicle performance, fuel efficiency, and overall service life while minimizing maintenance costs.
Trucks & Automotive Parts Classification
1. Engine Components
The engine is the heart of trucks and automobiles, responsible for generating power. Castings are used for intricate components like engine blocks, cylinder heads, and oil pans, which require complex shapes and superior casting performance. Forgings are used for high-strength, high-performance parts such as crankshafts, connecting rods, and pistons, where resistance to fatigue, high pressures, and high temperatures is essential.
· Castings: Engine block, Cylinder head, Oil pan
· Forgings: Crankshaft, Connecting rod, Piston
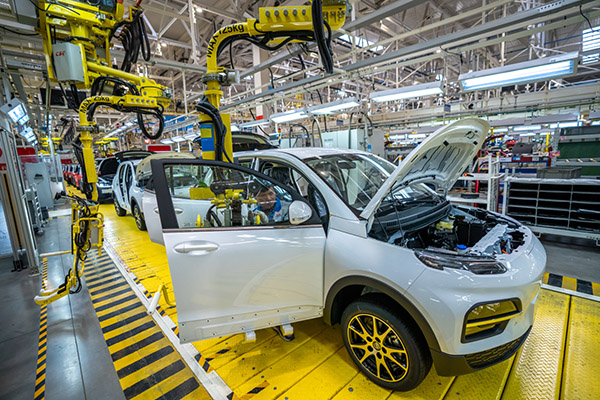

2. Suspension System
The suspension system is responsible for ensuring smooth handling and stability by absorbing shocks and vibrations from the road. Castings are typically used for suspension components like control arms and strut mounts due to their complex geometry. Forgings are employed in high-stress parts like suspension links, axle shafts, and steering knuckles, where durability and resistance to wear are crucial.
· Castings: Control arm, Strut mount
· Forgings: Suspension link, Axle shaft, Steering knuckle
3.Brake System
The brake system ensures the vehicle's ability to stop safely. Castings are used for brake components such as calipers, brackets, and housings, which need to absorb high heat and pressure. Forgings are used for parts like brake discs, brake drums, and master cylinders, as they must withstand high mechanical stress, wear, and thermal cycling.
· Castings: Brake caliper, Brake housing, Bracket
· Forgings: Brake disc, Brake drum, Master cylinder
4. Chassis and Frame Components
The chassis and frame provide structural support to the vehicle, ensuring the proper alignment of all components. Castings are employed for structural elements such as frame brackets, crossmembers, and subframes, which require high strength and rigidity. Forgings are used for heavy-duty components like suspension mounts, frame rails, and towing hooks, which must endure dynamic loads and provide stability.
· Castings: Frame bracket, Crossmember, Subframe
· Forgings: Frame rail, Towing hook, Suspension mount
5. Transmission System
The transmission system transmits power from the engine to the wheels, enabling the vehicle to operate efficiently at different speeds. Castings are used for complex transmission housings and gear cases, providing good structural integrity. Forgings are critical for components that need to transmit high torque and withstand dynamic loads, such as gears, shafts, and universal joints.
· Castings: Gearbox housing, Clutch housing, Gear case
· Forgings: Gear, Transmission shaft, Universal joint
6. Exhaust System
The exhaust system directs harmful gases away from the engine and improves vehicle efficiency. Castings are used for exhaust manifolds, turbocharger housings, and mufflers, where heat resistance, complex shapes, and durability are required. Forgings are used for components like exhaust pipes, flanges, and headers, which must handle high temperatures and stresses.
· Castings: Exhaust manifold, Turbo housing, Muffler
· Forgings: Exhaust pipe, Flange, Header
7. Steering System
The steering system controls the direction of the vehicle. Castings are used for parts such as steering housings and rack mounts, which require good strength and resistance to wear. Forgings are employed for critical components like steering shafts, pitman arms, and tie rods, which need to endure high stresses and ensure precise control and reliability.
· Castings: Steering housing, Rack mount
· Forgings: Steering shaft, Pitman arm, Tie rod
Available Materials For Trucks & Automotive Parts
Cast Iron
In vehicle manufacturing, cast iron is primarily used in engines, brake systems, and high-load bearing components, relying on its wear resistance and vibration absorption properties to ensure a smooth ride.
·Gray Cast Iron
Gray cast iron is often sand-cast into engine blocks, cylinder heads, brake discs, and exhaust manifolds. Its excellent vibration absorption properties reduce engine noise and ensure dimensional stability.
·Ductile Iron
Ductile iron is sand-cast and heat-treated for crankshafts, control arms, suspension mounts, and differential housings. It offers high strength and impact resistance, meeting the high-load requirements of vehicle chassis.
·Compacted Graphite Iron
Compacted graphite iron offers a balance of strength and toughness and is commonly used in heavy-duty diesel engine blocks and cylinder heads. Temperature-controlled casting achieves a uniform microstructure and improves fatigue resistance.
·Alloy Cast Iron
Alloy cast iron, after alloying and heat treatment, is used in high-temperature, wear-resistant components such as turbine housings, exhaust pipes, and wear bushings, ensuring long-term reliable operation.
Steel
Steel is used in vehicle manufacturing for load-bearing, transmission, and safety structures. High-strength, high-precision parts are produced through forging, stamping, welding, heat treatment, and machining. Steel production often incorporates heat treatment processes, such as quenching and tempering or surface hardening, to improve wear resistance and fatigue life, enabling the chassis, suspension, and drivetrain to withstand heavy loads, shock, and prolonged vibration.
· Carbon Steel
Carbon steel is forged and machined into steering knuckles, connecting rods, gears, drive shafts, and crankshafts, offering high strength and impact resistance, meeting the reliability requirements of long-term vehicle operation.
· Low-Alloy Steel
Low-alloy, high-strength steel is stamped and welded into vehicle body rails, cross members, suspension brackets, and bumper beams, reducing vehicle weight and improving collision energy absorption.
· Cast Steel
Cast steel is commonly used in sand casting or precision casting to produce differential cases, steering knuckle brackets, and heavy-duty chassis parts. Subsequent machining ensures assembly precision.
·High Manganese Steel
High manganese steel offers excellent wear resistance and is suitable for track shoes, bushings, and other high-wear parts in tracked vehicles, extending component life.
·Stainless Steel
Stainless steel is used in exhaust systems, mufflers, fuel lines, and fasteners. It offers excellent corrosion resistance and maintains reliability in long-term humid and high-temperature environments.
Aluminum Alloy
Aluminum alloys are used in vehicle manufacturing to reduce weight, improve performance, and enhance corrosion resistance. They are commonly manufactured into various parts through die-casting, forging, extrusion, welding, and machining. Aluminum alloys not only achieve lightweighting goals, but also ensure component strength, toughness, and assembly precision through the proper selection of processes and heat treatments. This ensures reliable performance in both everyday driving and extreme conditions for cars, motorcycles, and bicycles.
· Forged Aluminum Alloys
Forged aluminum alloys feature continuous, streamlined fibers, high strength, and excellent toughness. They are used in high-stress components such as suspension control arms, wheels, and steering knuckles in racing and high-performance vehicles, motorcycle frames, and bicycle cranks and hubs, ensuring lightweight yet withstanding impact and fatigue loads.
· Aluminum-Silicon Alloys
Aluminum-silicon alloys are suitable for die-casting engine blocks, transmission housings, clutch housings, oil pans, and motor housings. They offer excellent thermal conductivity and wear resistance, ensuring heat dissipation and stable engine operation.
·Aluminum-magnesium alloys
Aluminum-magnesium alloys have low density and excellent corrosion resistance. They are often extruded and welded into vehicle doors, bumper beams, roof racks, motorcycle fuel tanks, and lightweight subframes, enhancing vehicle strength and extending vehicle life.
·High-strength aluminum alloys
High-strength aluminum alloys undergo solution and aging heat treatments and are machined into suspension arms, steering components, lightweight wheels, and high-stress connectors. They are lighter than steel while still meeting load-bearing requirements.
·Aluminum extrusions
Aluminum extrusions are extruded and machined into electric vehicle battery boxes, radiators, frame structures, and bicycle frames. Anodizing or painting enhances both appearance and corrosion resistance.
Other Metal Alloys
Vehicle manufacturing also uses a variety of specialty metals to meet electrical conductivity, wear resistance, and lightweight requirements, as well as specific performance requirements such as high-temperature resistance, corrosion resistance, or wear resistance. These alloys, due to their unique properties, offer exceptional strength, heat resistance, or lightweight properties in demanding applications.
·Magnesium Alloys
Magnesium alloys are extremely lightweight and, through die-casting, can significantly reduce vehicle weight in steering wheel frames, instrument panel brackets, and seat frames.
·Titanium Alloys
Titanium alloys offer high strength and corrosion resistance and are commonly used in high-performance exhaust systems, suspension bolts, and racing components, enhancing durability and performance.
·Copper and Copper Alloys
Copper and copper alloys are used in radiators, water pipes, busbars, connectors, and motor windings. Extrusion and machining ensure efficient electrical and thermal conductivity.
Bronze, with its excellent wear resistance, is used in plain bearings, bushings, and synchronizer rings, ensuring smooth shifting in transmission systems.
Brass is easy to machine and is commonly used in brake line connectors, valve bodies, and electrical terminals, offering ease of assembly and corrosion resistance.
Cast Iron
In vehicle manufacturing, cast iron is primarily used in engines, brake systems, and high-load bearing components, relying on its wear resistance and vibration absorption properties to ensure a smooth ride.
·Gray Cast Iron
Gray cast iron is often sand-cast into engine blocks, cylinder heads, brake discs, and exhaust manifolds. Its excellent vibration absorption properties reduce engine noise and ensure dimensional stability.
·Ductile Iron
Ductile iron is sand-cast and heat-treated for crankshafts, control arms, suspension mounts, and differential housings. It offers high strength and impact resistance, meeting the high-load requirements of vehicle chassis.
·Compacted Graphite Iron
Compacted graphite iron offers a balance of strength and toughness and is commonly used in heavy-duty diesel engine blocks and cylinder heads. Temperature-controlled casting achieves a uniform microstructure and improves fatigue resistance.
·Alloy Cast Iron
Alloy cast iron, after alloying and heat treatment, is used in high-temperature, wear-resistant components such as turbine housings, exhaust pipes, and wear bushings, ensuring long-term reliable operation.
Steel
Steel is used in vehicle manufacturing for load-bearing, transmission, and safety structures. High-strength, high-precision parts are produced through forging, stamping, welding, heat treatment, and machining. Steel production often incorporates heat treatment processes, such as quenching and tempering or surface hardening, to improve wear resistance and fatigue life, enabling the chassis, suspension, and drivetrain to withstand heavy loads, shock, and prolonged vibration.
· Carbon Steel
Carbon steel is forged and machined into steering knuckles, connecting rods, gears, drive shafts, and crankshafts, offering high strength and impact resistance, meeting the reliability requirements of long-term vehicle operation.
· Low-Alloy Steel
Low-alloy, high-strength steel is stamped and welded into vehicle body rails, cross members, suspension brackets, and bumper beams, reducing vehicle weight and improving collision energy absorption.
· Cast Steel
Cast steel is commonly used in sand casting or precision casting to produce differential cases, steering knuckle brackets, and heavy-duty chassis parts. Subsequent machining ensures assembly precision.
·High Manganese Steel
High manganese steel offers excellent wear resistance and is suitable for track shoes, bushings, and other high-wear parts in tracked vehicles, extending component life.
·Stainless Steel
Stainless steel is used in exhaust systems, mufflers, fuel lines, and fasteners. It offers excellent corrosion resistance and maintains reliability in long-term humid and high-temperature environments.
Aluminum Alloy
Aluminum alloys are used in vehicle manufacturing to reduce weight, improve performance, and enhance corrosion resistance. They are commonly manufactured into various parts through die-casting, forging, extrusion, welding, and machining. Aluminum alloys not only achieve lightweighting goals, but also ensure component strength, toughness, and assembly precision through the proper selection of processes and heat treatments. This ensures reliable performance in both everyday driving and extreme conditions for cars, motorcycles, and bicycles.
· Forged Aluminum Alloys
Forged aluminum alloys feature continuous, streamlined fibers, high strength, and excellent toughness. They are used in high-stress components such as suspension control arms, wheels, and steering knuckles in racing and high-performance vehicles, motorcycle frames, and bicycle cranks and hubs, ensuring lightweight yet withstanding impact and fatigue loads.
· Aluminum-Silicon Alloys
Aluminum-silicon alloys are suitable for die-casting engine blocks, transmission housings, clutch housings, oil pans, and motor housings. They offer excellent thermal conductivity and wear resistance, ensuring heat dissipation and stable engine operation.
·Aluminum-magnesium alloys
Aluminum-magnesium alloys have low density and excellent corrosion resistance. They are often extruded and welded into vehicle doors, bumper beams, roof racks, motorcycle fuel tanks, and lightweight subframes, enhancing vehicle strength and extending vehicle life.
·High-strength aluminum alloys
High-strength aluminum alloys undergo solution and aging heat treatments and are machined into suspension arms, steering components, lightweight wheels, and high-stress connectors. They are lighter than steel while still meeting load-bearing requirements.
·Aluminum extrusions
Aluminum extrusions are extruded and machined into electric vehicle battery boxes, radiators, frame structures, and bicycle frames. Anodizing or painting enhances both appearance and corrosion resistance.
Other Metal Alloys
Vehicle manufacturing also uses a variety of specialty metals to meet electrical conductivity, wear resistance, and lightweight requirements, as well as specific performance requirements such as high-temperature resistance, corrosion resistance, or wear resistance. These alloys, due to their unique properties, offer exceptional strength, heat resistance, or lightweight properties in demanding applications.
·Magnesium Alloys
Magnesium alloys are extremely lightweight and, through die-casting, can significantly reduce vehicle weight in steering wheel frames, instrument panel brackets, and seat frames.
·Titanium Alloys
Titanium alloys offer high strength and corrosion resistance and are commonly used in high-performance exhaust systems, suspension bolts, and racing components, enhancing durability and performance.
·Copper and Copper Alloys
Copper and copper alloys are used in radiators, water pipes, busbars, connectors, and motor windings. Extrusion and machining ensure efficient electrical and thermal conductivity.
Bronze, with its excellent wear resistance, is used in plain bearings, bushings, and synchronizer rings, ensuring smooth shifting in transmission systems.
Brass is easy to machine and is commonly used in brake line connectors, valve bodies, and electrical terminals, offering ease of assembly and corrosion resistance.
How To Customize Trucks & Automotive Parts
3D Drawings
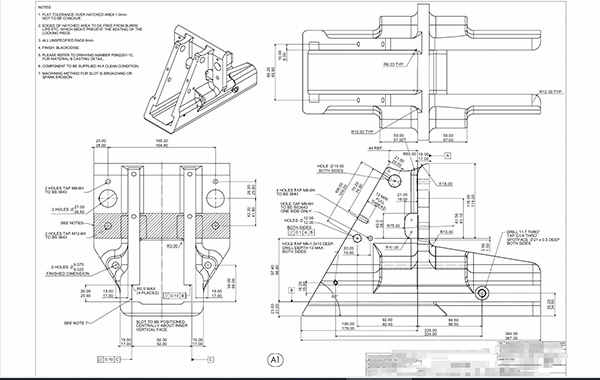
Processing Drawings

Sample
1. Provide Detailed Design Documents Or Samples
2. Confirm Material/Process/Performance
3. Make Production Molds And Samples
4. Comprehensive Sample Inspection
5. Mass Production
6. Post-production Parts Multiple Quality Inspections
1. Provide Detailed Design Documents Or Samples
2. Confirm Material/Process/Performance
3. Make Production Molds And Samples
4. Comprehensive Sample Inspection
5. Mass Production
6. Post-production Parts Multiple Quality Inspections
Custom Processing Of Trucks & Automotive Parts

Casting
In the truck and automotive industries, casting processes are used to manufacture parts such as engine blocks, transmissions and axle housings with complex geometry and structural integrity, improving the durability and performance of automotive components under high load, temperature and vibration conditions.

Forging
In the truck and automobile industries, forging processes are used to produce key components such as crankshafts, gears, suspension components and connecting rods. Forged powertrain and chassis components have excellent fatigue resistance, strength and toughness, improving the stability and long-term durability of the vehicle.
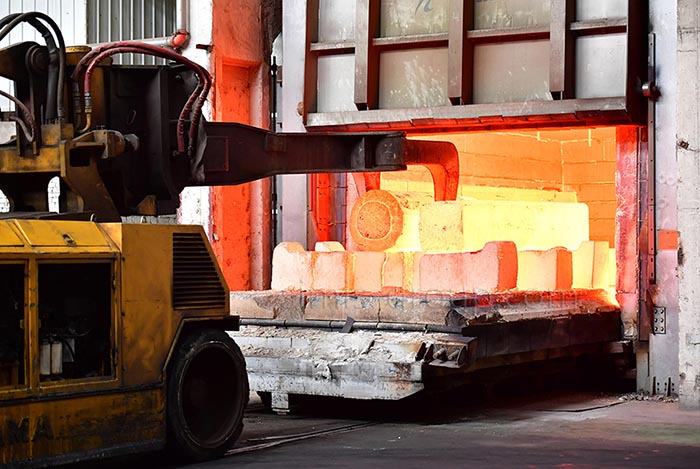

Heat Treatment
In the truck and automotive industries, heat treatment processes enhance the performance of parts such as gears, shafts, brake rotors and valve springs, improving wear resistance and fatigue strength, ensuring components perform reliably over a long period of time, reducing maintenance and improving safety, especially in high-performance or heavy-duty vehicles.
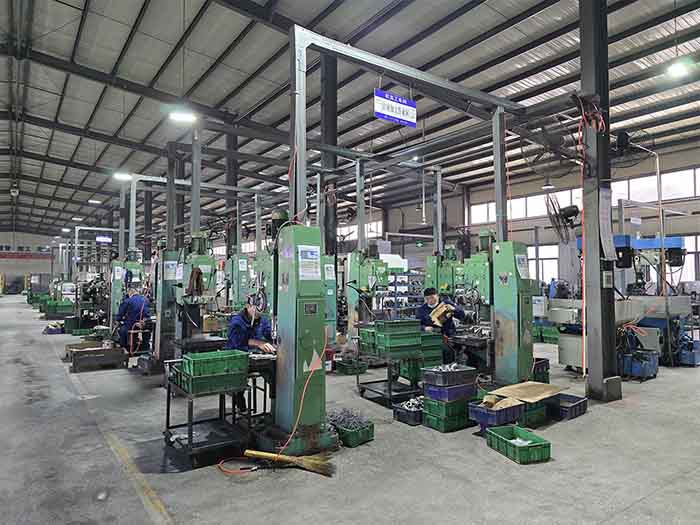

Machining
In the truck and automotive industries, machining is used to produce high-precision components such as engine parts, cylinder heads and turbochargers. Machining ensures that parts meet tight tolerances, ensuring optimal performance, fuel efficiency and safety.

Sheet Metal Fabrication
In the truck and automotive industries, sheet metal fabrication is used to manufacture the exterior structure of vehicles, including doors, hoods and roofs, as well as interior components and structural supports that contribute to the strength, safety and aesthetics of the vehicle.

Surface Treatment
In the truck and automotive industries, surface treatments are applied to components such as brake components, exhaust systems and suspension parts to improve corrosion resistance, wear resistance and overall durability, protect components from environmental factors, reduce maintenance, extend the service life of automotive components and ensure reliable performance in various driving conditions.









































