Manufacturing Process of Cast Aluminum Parts

Aluminum Sand Casting
Aluminum sand casting uses sand as the casting material, then pours molten aluminum into the casting mold, takes out the casting after cooling, cleans and post-processes it.
· The mold manufacturing cost is low and can be used many times
· Casts large and medium-sized aluminum castings with complex shapes and large sizes.
· Suitable for small, medium and large batch production.

Aluminum Die Casting
Aluminum die casting is a process that uses high pressure to inject molten aluminum alloy into a metal mold cavity to quickly fill the cavity and solidify. It is suitable for mass production of thin-walled, complex, and high-precision parts.
· The aluminum casting surface is smooth and the dimensional accuracy is high.
· The production cycle is short and suitable for mass production.
· The metal loss is small and the cooling in the mold is fast.

Aluminum Gravity Casting
Aluminum gravity casting usually uses metal molds, the aluminum solution solidifies and forms under natural conditions. It is suitable for parts of medium complexity.
· The mold cost is low and suitable for small and medium batch production.
· Larger aluminum alloy parts can be produced with better density.
· The parts produced are relatively cheap.

Aluminum Investment Casting
Aluminum investment casting uses soluble or combustible casting molds (such as wax molds) to make castings, and is often used to make aluminum parts with complex shapes and high precision requirements.
· High surface quality
· No need for a lot of post-processing
· Suitable for small batches and high precision parts

Machining
Machining is a post-processing process for aluminum castings, which improves the accuracy, surface quality and functionality of aluminum alloy castings through fine processing.
· Optimize appearance quality
· Improve aluminum part structure and function
· Process thin walls and complex shapes

Surface Treatment
Surface treatment can transform the surface of aluminum castings by physical, chemical or mechanical means to improve the surface quality of castings, increase their durability, and improve appearance and functionality.
· Improve surface hardness
· Improve appearance and improve dimensional accuracy
· Improve adhesion and corrosion resistance
Different Materials of Aluminum Alloy Castings
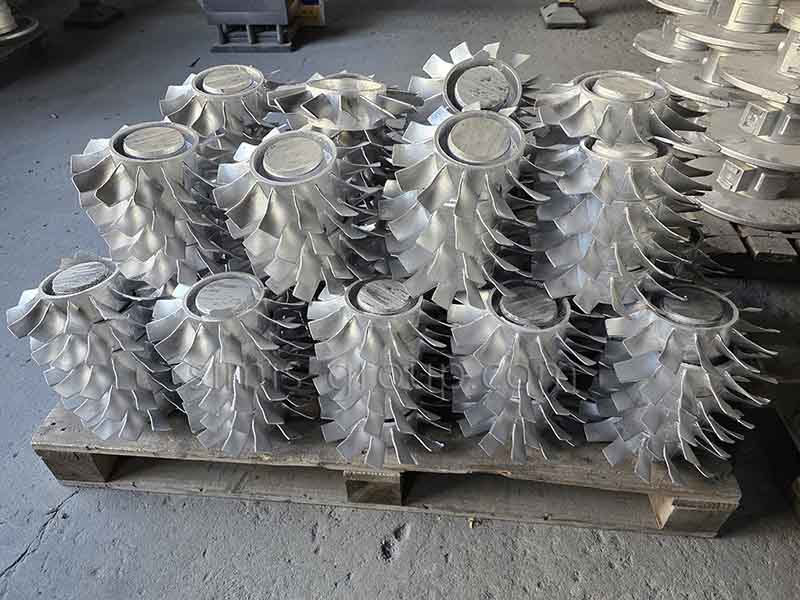
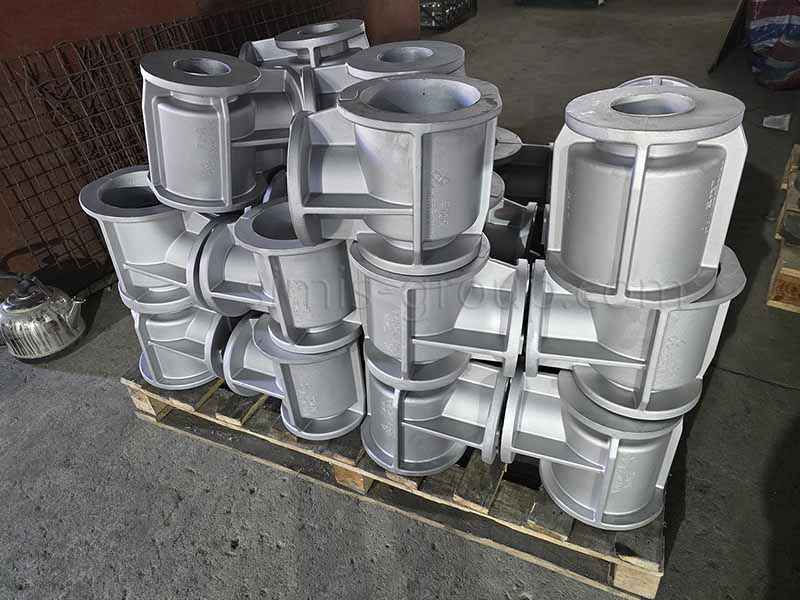
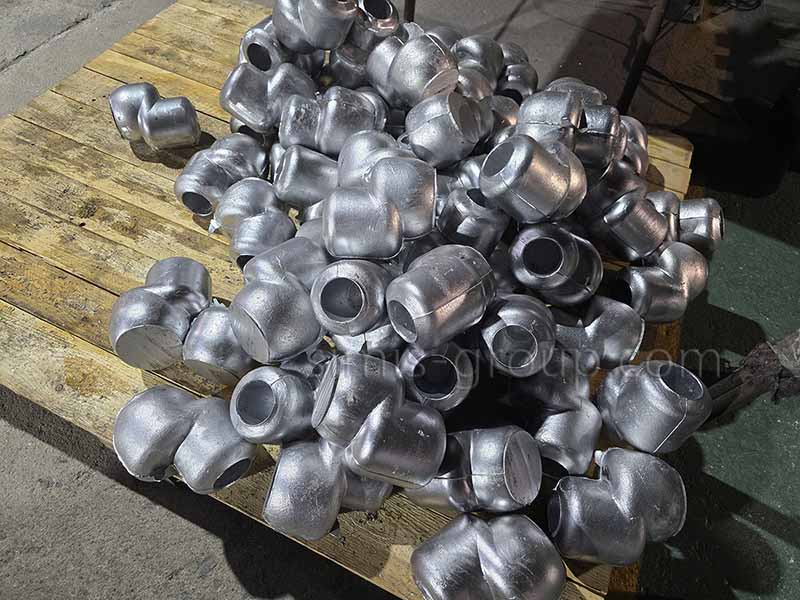



1. Aluminum-Silicon Alloy
Aluminum-Silicon alloy casting is used to produce lightweight, complex components with excellent castability and a good strength-to-weight ratio. Adding silicon to aluminum significantly improves fluidity, lowers melting temperature, and minimizes shrinkage. Other elements, such as magnesium (Mg), enable precipitation hardening (via T5/T6/T7 heat treatments), while copper (Cu) increases strength but slightly reduces corrosion resistance. Al-Si alloys are the most widely used cast aluminum materials across various industries.
· Excellent Castability: Silicon markedly improves molten metal fluidity, allowing for the production of thin-walled and intricate castings with fine detail.
· Good Corrosion Resistance: Forms a protective oxide layer, offering strong resistance to atmospheric and many chemical environments.
· High Strength-to-Weight Ratio: Provides good mechanical properties at a low density, essential for weight-sensitive applications.
· Excellent Machinability: Most Al-Si alloys are relatively soft and easy to machine, offering good surface finishes.
· Good Thermal Conductivity: Well-suited for applications requiring heat dissipation, such as engine components and electronic housings.
Aluminum-Silicon Alloy Castings by Simis Aluminum Foundry:
Engine cylinder heads, intake manifolds, and pistons; transmission cases and housings; pump bodies and impellers; architectural fittings and decorative hardware; electronic enclosures and heat sinks; automotive wheels and structural components.
Aluminum-Silicon Alloy Casting Grades Used by Simis Aluminum Foundry:
· Hypoeutectic Alloys (Silicon content 5% - 10%)
Common Applications: Structural automotive parts (cylinder heads, blocks), aerospace components, high-strength machinery parts.
Common Grades: A356.0 (AlSi7Mg), A357.0 (AlSi7Mg0.5), 319.0 (AlSi5Cu3)
· Eutectic Alloys (Silicon content ~11% - 13%)
Common Applications: Complex, thin-walled castings, pump housings, valve bodies, and other parts where leak-tightness is critical.
Common Grades: 413.0 (AlSi12), A413.0 (AlSi12), 443.0 (AlSi5Fe)
· Hypereutectic Alloys (Silicon content > 14%)
Common Applications: Engine pistons, cylinder liners, brake rotors, and other components requiring high wear resistance and stability at elevated temperatures.
Common Grades: 390.0 (AlSi17Cu5Mg), A390.0 (AlSi17Cu5Mg)
2. Aluminum-Copper Alloy
Aluminum-Copper alloys are used to produce high-strength components, prioritizing mechanical properties over castability. These alloys are among the strongest cast aluminum materials and offer excellent heat-treatable properties, making them ideal for aerospace and high-performance engineering structural applications. While their corrosion resistance is not as good as that of Al-Si or Al-Mg alloys, this can be addressed through anodizing or other surface treatments.
· High Strength at Room and Elevated Temperatures: Achieve the highest strength levels of all cast aluminum alloys after heat treatment, and retain strength better than other systems at temperatures up to ~200°C.
· Excellent Response to Heat Treatment: Respond strongly to solution treatment and aging (T5, T6, T7 tempers), enabling significant enhancement of mechanical properties.
· Good Machinability: Generally good machining characteristics, producing clean chips and good surface finishes.
· Moderate Corrosion Resistance: Generally inferior to Al-Si alloys in corrosive environments, often requiring protective coatings for harsh service.
· Fair Castability: More susceptible to hot tearing and shrinkage than Al-Si alloys, requiring careful gating and risering design.
Aluminum-Copper Alloy Castings by Simis Aluminum Foundry:
Aircraft structural fittings and brackets; high-performance automotive suspension components; cylinder heads for air-cooled engines; high-strength robotic arms and machinery parts.
Aluminum-Copper Alloy Casting Grades Used by Simis Aluminum Foundry:
· Binary Al-Cu Alloys
Common Applications: General high-strength castings, structural components, and parts requiring good toughness.
Common Grades: 295.0 (AlCu5Si3), 296.0 (AlCu5Si3)
· Al-Cu with Silicon Addition
Common Applications: Complex, high-strength castings, such as cylinder heads and crankcases.
Common Grades: 319.0 (AlSi6Cu4), 355.0 (AlSi5Cu1)
· High-Strength Al-Cu Alloys (with Mg, Mn, Cd additions)
Common Applications: Critical aerospace components, highest strength-to-weight ratio applications.
Common Grades: 201.0 (AlCu4TiMg), 206.0 (AlCu5Ni2Mg)
3. Aluminum-Magnesium alloy
Aluminum-Magnesium alloys offer excellent corrosion resistance, high ductility, and a smooth surface finish. They are widely used in marine, offshore, chemical, and corrosive environments. The corrosion resistance of aluminum-magnesium alloys stems from the protective magnesium oxide film that forms on their surface.
· Exceptional Corrosion Resistance: Exhibits outstanding resistance to seawater and industrial chemicals, forming a protective oxide film that is highly stable in corrosive environments.
· Good Machinability and Surface Finish: Machines to excellent surface quality and accepts anodizing and other surface treatments better than other aluminum casting alloys.
· High Ductility and Impact Strength: Maintains excellent toughness and energy absorption characteristics, making it ideal for shock-loaded components.
· Moderate Strength Properties: Generally offers lower strength than Al-Cu and heat-treated Al-Si alloys, but provides better toughness and damage tolerance.
· Good Weldability and Repair Characteristics: Can be readily welded and repaired using standard techniques without significant loss of properties.
Aluminum-Magnesium Alloy Castings by Simis Aluminum Foundry:
Marine hardware and boat components; chemical processing equipment; food and beverage handling parts; architectural and decorative fittings; pressure vessels for corrosive services.
Aluminum-Magnesium Alloy Casting Grades Used by Simis Aluminum Foundry:
· Low Magnesium Alloys (Mg content 3-5%)
Common Applications: General corrosion-resistant castings, marine fittings, architectural components, and food processing equipment.
Common Grades: 514.0 (AlMg3Si), 515.0 (AlMg5)
· Medium Magnesium Alloys (Mg content 5-7%)
Common Applications: Marine structural components, pump bodies, valve housings, and chemical processing equipment.
Common Grades: 520.0 (AlMg10), 535.0 (AlMg5Cr)
· High Magnesium Alloys (Mg content 7-10%)
Common Applications: High-strength marine components, naval architecture, and severe service corrosion applications.
Common Grades: 518.0 (AlMg8), 508.0 (AlMg4Cr)
4. Other aluminum alloys
Simis Aluminum Alloy Foundry can cast other common aluminum alloy materials, including aluminum-zinc alloy, aluminum-manganese alloy and aluminum-titanium alloy. These alloys can be used to provide specific performance requirements that cannot be met by aluminum-silicon alloy, aluminum-copper alloy or aluminum-magnesium alloy, such as providing excellent performance in high temperature applications, controlled thermal expansion or special applications requiring a unique combination of properties to meet the special needs of various industrial fields.
· High Temperature Performance: Maintain strength and stability at elevated temperatures (200-400°C) where conventional aluminum alloys would soften.
· Controlled Thermal Expansion: Offer specific thermal expansion characteristics matching other materials like steels or ceramics.
· Specialized Wear Characteristics: Provide unique tribological properties for specific bearing or wear applications.
· Complex Property Combinations: Engineered to meet multiple demanding requirements simultaneously.
Specialty Aluminum Alloy Castings by Simis Aluminum Foundry:
Piston and cylinder head components for internal combustion engines; precision instrumentation and optical mounting systems; bearing sleeves and bushings; aerospace components requiring thermal stability; electronic packaging with specific thermal management needs.
Specialty Aluminum Alloy Casting Categories Used by Simis Aluminum Foundry:
· Aluminum-Tin (Al-Sn) Bearing Alloys
Common Applications: Engine connecting rod bearings, main bearings, and other high-load sliding contacts.
Common Grades: ASTM B179 Grade A850.0 (AlSn20Cu1), AS13 (AlSn6Si1Cu1)
· Aluminum-Zinc (Al-Zn) Alloys
Common Applications: Architectural fittings, decorative hardware, and general engineering components.
Common Grades: 712.0 (AlZn5Mg), 713.0 (AlZn7Mg)
· Aluminum with High Iron and Manganese (Heat-Resistant)
Common Applications: Automotive turbocharger housings, piston crowns, and other components operating at elevated temperatures.
Common Grades: A390.0 (AlSi17Cu5Mg) with high iron variants, 392.0 (AlSi19MgCu)
· Aluminum-Manganese (Al-Mn) Alloys
Common Applications: Chemical processing equipment, food and beverage handling parts, heat exchangers, marine applications, and architectural components requiring good formability and welding characteristics.
Common Grades: 3003 (AlMn1Cu), 3105 (AlMn0.5Mg0.5)
1. Aluminum-Silicon Alloy
Aluminum-Silicon alloy casting is used to produce lightweight, complex components with excellent castability and a good strength-to-weight ratio. Adding silicon to aluminum significantly improves fluidity, lowers melting temperature, and minimizes shrinkage. Other elements, such as magnesium (Mg), enable precipitation hardening (via T5/T6/T7 heat treatments), while copper (Cu) increases strength but slightly reduces corrosion resistance. Al-Si alloys are the most widely used cast aluminum materials across various industries.
· Excellent Castability: Silicon markedly improves molten metal fluidity, allowing for the production of thin-walled and intricate castings with fine detail.
· Good Corrosion Resistance: Forms a protective oxide layer, offering strong resistance to atmospheric and many chemical environments.
· High Strength-to-Weight Ratio: Provides good mechanical properties at a low density, essential for weight-sensitive applications.
· Excellent Machinability: Most Al-Si alloys are relatively soft and easy to machine, offering good surface finishes.
· Good Thermal Conductivity: Well-suited for applications requiring heat dissipation, such as engine components and electronic housings.
Aluminum-Silicon Alloy Castings by Simis Aluminum Foundry:
Engine cylinder heads, intake manifolds, and pistons; transmission cases and housings; pump bodies and impellers; architectural fittings and decorative hardware; electronic enclosures and heat sinks; automotive wheels and structural components.
Aluminum-Silicon Alloy Casting Grades Used by Simis Aluminum Foundry:
· Hypoeutectic Alloys (Silicon content 5% - 10%)
Common Applications: Structural automotive parts (cylinder heads, blocks), aerospace components, high-strength machinery parts.
Common Grades: A356.0 (AlSi7Mg), A357.0 (AlSi7Mg0.5), 319.0 (AlSi5Cu3)
· Eutectic Alloys (Silicon content ~11% - 13%)
Common Applications: Complex, thin-walled castings, pump housings, valve bodies, and other parts where leak-tightness is critical.
Common Grades: 413.0 (AlSi12), A413.0 (AlSi12), 443.0 (AlSi5Fe)
· Hypereutectic Alloys (Silicon content > 14%)
Common Applications: Engine pistons, cylinder liners, brake rotors, and other components requiring high wear resistance and stability at elevated temperatures.
Common Grades: 390.0 (AlSi17Cu5Mg), A390.0 (AlSi17Cu5Mg)
2. Aluminum-Copper Alloy
Aluminum-Copper alloys are used to produce high-strength components, prioritizing mechanical properties over castability. These alloys are among the strongest cast aluminum materials and offer excellent heat-treatable properties, making them ideal for aerospace and high-performance engineering structural applications. While their corrosion resistance is not as good as that of Al-Si or Al-Mg alloys, this can be addressed through anodizing or other surface treatments.
· High Strength at Room and Elevated Temperatures: Achieve the highest strength levels of all cast aluminum alloys after heat treatment, and retain strength better than other systems at temperatures up to ~200°C.
· Excellent Response to Heat Treatment: Respond strongly to solution treatment and aging (T5, T6, T7 tempers), enabling significant enhancement of mechanical properties.
· Good Machinability: Generally good machining characteristics, producing clean chips and good surface finishes.
· Moderate Corrosion Resistance: Generally inferior to Al-Si alloys in corrosive environments, often requiring protective coatings for harsh service.
· Fair Castability: More susceptible to hot tearing and shrinkage than Al-Si alloys, requiring careful gating and risering design.
Aluminum-Copper Alloy Castings by Simis Aluminum Foundry:
Aircraft structural fittings and brackets; high-performance automotive suspension components; cylinder heads for air-cooled engines; high-strength robotic arms and machinery parts.
Aluminum-Copper Alloy Casting Grades Used by Simis Aluminum Foundry:
· Binary Al-Cu Alloys
Common Applications: General high-strength castings, structural components, and parts requiring good toughness.
Common Grades: 295.0 (AlCu5Si3), 296.0 (AlCu5Si3)
· Al-Cu with Silicon Addition
Common Applications: Complex, high-strength castings, such as cylinder heads and crankcases.
Common Grades: 319.0 (AlSi6Cu4), 355.0 (AlSi5Cu1)
· High-Strength Al-Cu Alloys (with Mg, Mn, Cd additions)
Common Applications: Critical aerospace components, highest strength-to-weight ratio applications.
Common Grades: 201.0 (AlCu4TiMg), 206.0 (AlCu5Ni2Mg)
3. Aluminum-Magnesium alloy
Aluminum-Magnesium alloys offer excellent corrosion resistance, high ductility, and a smooth surface finish. They are widely used in marine, offshore, chemical, and corrosive environments. The corrosion resistance of aluminum-magnesium alloys stems from the protective magnesium oxide film that forms on their surface.
· Exceptional Corrosion Resistance: Exhibits outstanding resistance to seawater and industrial chemicals, forming a protective oxide film that is highly stable in corrosive environments.
· Good Machinability and Surface Finish: Machines to excellent surface quality and accepts anodizing and other surface treatments better than other aluminum casting alloys.
· High Ductility and Impact Strength: Maintains excellent toughness and energy absorption characteristics, making it ideal for shock-loaded components.
· Moderate Strength Properties: Generally offers lower strength than Al-Cu and heat-treated Al-Si alloys, but provides better toughness and damage tolerance.
· Good Weldability and Repair Characteristics: Can be readily welded and repaired using standard techniques without significant loss of properties.
Aluminum-Magnesium Alloy Castings by Simis Aluminum Foundry:
Marine hardware and boat components; chemical processing equipment; food and beverage handling parts; architectural and decorative fittings; pressure vessels for corrosive services.
Aluminum-Magnesium Alloy Casting Grades Used by Simis Aluminum Foundry:
· Low Magnesium Alloys (Mg content 3-5%)
Common Applications: General corrosion-resistant castings, marine fittings, architectural components, and food processing equipment.
Common Grades: 514.0 (AlMg3Si), 515.0 (AlMg5)
· Medium Magnesium Alloys (Mg content 5-7%)
Common Applications: Marine structural components, pump bodies, valve housings, and chemical processing equipment.
Common Grades: 520.0 (AlMg10), 535.0 (AlMg5Cr)
· High Magnesium Alloys (Mg content 7-10%)
Common Applications: High-strength marine components, naval architecture, and severe service corrosion applications.
Common Grades: 518.0 (AlMg8), 508.0 (AlMg4Cr)
4. Other aluminum alloys
Simis Aluminum Alloy Foundry can cast other common aluminum alloy materials, including aluminum-zinc alloy, aluminum-manganese alloy and aluminum-titanium alloy. These alloys can be used to provide specific performance requirements that cannot be met by aluminum-silicon alloy, aluminum-copper alloy or aluminum-magnesium alloy, such as providing excellent performance in high temperature applications, controlled thermal expansion or special applications requiring a unique combination of properties to meet the special needs of various industrial fields.
· High Temperature Performance: Maintain strength and stability at elevated temperatures (200-400°C) where conventional aluminum alloys would soften.
· Controlled Thermal Expansion: Offer specific thermal expansion characteristics matching other materials like steels or ceramics.
· Specialized Wear Characteristics: Provide unique tribological properties for specific bearing or wear applications.
· Complex Property Combinations: Engineered to meet multiple demanding requirements simultaneously.
Specialty Aluminum Alloy Castings by Simis Aluminum Foundry:
Piston and cylinder head components for internal combustion engines; precision instrumentation and optical mounting systems; bearing sleeves and bushings; aerospace components requiring thermal stability; electronic packaging with specific thermal management needs.
Specialty Aluminum Alloy Casting Categories Used by Simis Aluminum Foundry:
· Aluminum-Tin (Al-Sn) Bearing Alloys
Common Applications: Engine connecting rod bearings, main bearings, and other high-load sliding contacts.
Common Grades: ASTM B179 Grade A850.0 (AlSn20Cu1), AS13 (AlSn6Si1Cu1)
· Aluminum-Zinc (Al-Zn) Alloys
Common Applications: Architectural fittings, decorative hardware, and general engineering components.
Common Grades: 712.0 (AlZn5Mg), 713.0 (AlZn7Mg)
· Aluminum with High Iron and Manganese (Heat-Resistant)
Common Applications: Automotive turbocharger housings, piston crowns, and other components operating at elevated temperatures.
Common Grades: A390.0 (AlSi17Cu5Mg) with high iron variants, 392.0 (AlSi19MgCu)
· Aluminum-Manganese (Al-Mn) Alloys
Common Applications: Chemical processing equipment, food and beverage handling parts, heat exchangers, marine applications, and architectural components requiring good formability and welding characteristics.
Common Grades: 3003 (AlMn1Cu), 3105 (AlMn0.5Mg0.5)
Application of Aluminum Alloy Castings
Custom Aluminum Castings by Simis Foundry
Aluminum Alloy Castings Company's Custom Steps


Confirm customization requirements
1. Provide detailed design documents or samples of parts
The engineering team will review the 3D drawings (CAD models) and corresponding processing plans provided by customers to ensure that they meet manufacturing requirements.
Samples: If customers provide samples, we can also produce according to samples.
2. Confirm the material of the aluminum castings
Choose the appropriate aluminum alloy material according to the use environment, technical requirements or customer requirements of the parts. We will give reasonable suggestions based on the price, mechanical properties, wear resistance, corrosion resistance, etc. of the materials.
3. Confirm the casting process
Determine the appropriate aluminum alloy casting process based on customer needs and part price, shape, size, precision, material, etc.
4. Confirm the requirements for various product attributes
Confirm the various performance requirements of the parts under the casting process and materials, such as strength, hardness, wear resistance, corrosion resistance, etc.
According to the drawings and product requirements, confirm the dimensional tolerance and precision requirements, surface roughness, appearance quality and other requirements of the product.
5. Make molds and samples
Make casting molds that meet the requirements according to the drawings or samples provided by the customer; and cast the selected casting materials through the corresponding process to produce the first batch of cast aluminum samples
6. Comprehensive inspection of samples
The produced samples will be fully inspected, including size and tolerance inspection, performance test, chemical composition analysis, non-destructive testing and other test reports.
7. Mass production
After the samples are confirmed and approved by the customer, arrange the mass production plan according to the order requirements and prepare the production materials.
Production and quality control
8. Quality control in mass production
We implement strict quality control measures during the production process to ensure that the quality of each aluminum alloy casting in mass production meets customer requirements.
Production process quality monitoring: Regular sampling during the production process to check the size, appearance, physical properties, etc. of aluminum alloy castings to ensure the consistency of each batch of parts.
Equipment inspection: Regularly inspect production equipment to avoid production deviations due to equipment failure.
9. Product quality inspection after production
Multiple inspections by multiple people: We will arrange different inspectors to conduct multiple random inspections on the final product, including dimensional accuracy, surface quality, strength, hardness, etc., to ensure that the cast aluminum parts produced meet customer requirements.
Quality inspection report: Provide a detailed quality inspection report for each aluminum alloy casting inspected.
10. Parts packaging and delivery
Packaging: For parts that pass the quality inspection, pack and ship them, choose the appropriate packaging method and the appropriate logistics method (such as air, sea, and land transportation) to avoid damage during transportation and deliver them to customers on time.




If you want to custom parts, please send me the design drawings and 3D drawings of theparts you want to customize by email, and we will calculate an accurate price for you bylooking at the detailed part parameters and 3D model.







































