Custom Metal Parts For Agricultural Machinery
Custom metal parts for agricultural machinery can optimize the performance, durability and efficiency of various agricultural equipment. Common custom metal parts include gears, shafts, plows, harrow blades and various structural parts, which can be tailored to the specific operating requirements of agricultural machinery such as tractors, harvesters, seeders and tillers, such as high load-bearing capacity, wear and corrosion resistance, and the ability to withstand harsh environmental conditions. Customized design and production ensure that these metal parts precisely meet the design and performance specifications of the machinery, ultimately helping to improve efficiency, reduce downtime and reduce maintenance costs in the agricultural sector. The manufacturing of agricultural machinery parts typically involves processes such as casting/forging, machining and heat treatment to enhance material properties.
Agricultural Machinery Parts Classification
1. Transmission System
The transmission system is crucial in transmitting the engine power to the working parts of agricultural machinery. Castings are commonly used for producing complex housings and structural components, which provide stability and facilitate efficient production. Forgings, on the other hand, are used for high-strength components such as gears and shafts, which are subjected to high torque and dynamic loads, ensuring the reliability, precision, and durability of the system.
· Castings: Gearbox housing, Clutch housing, Sprocket seat
· Forgings: Gear, Transmission shaft, Universal joint, Sprocket
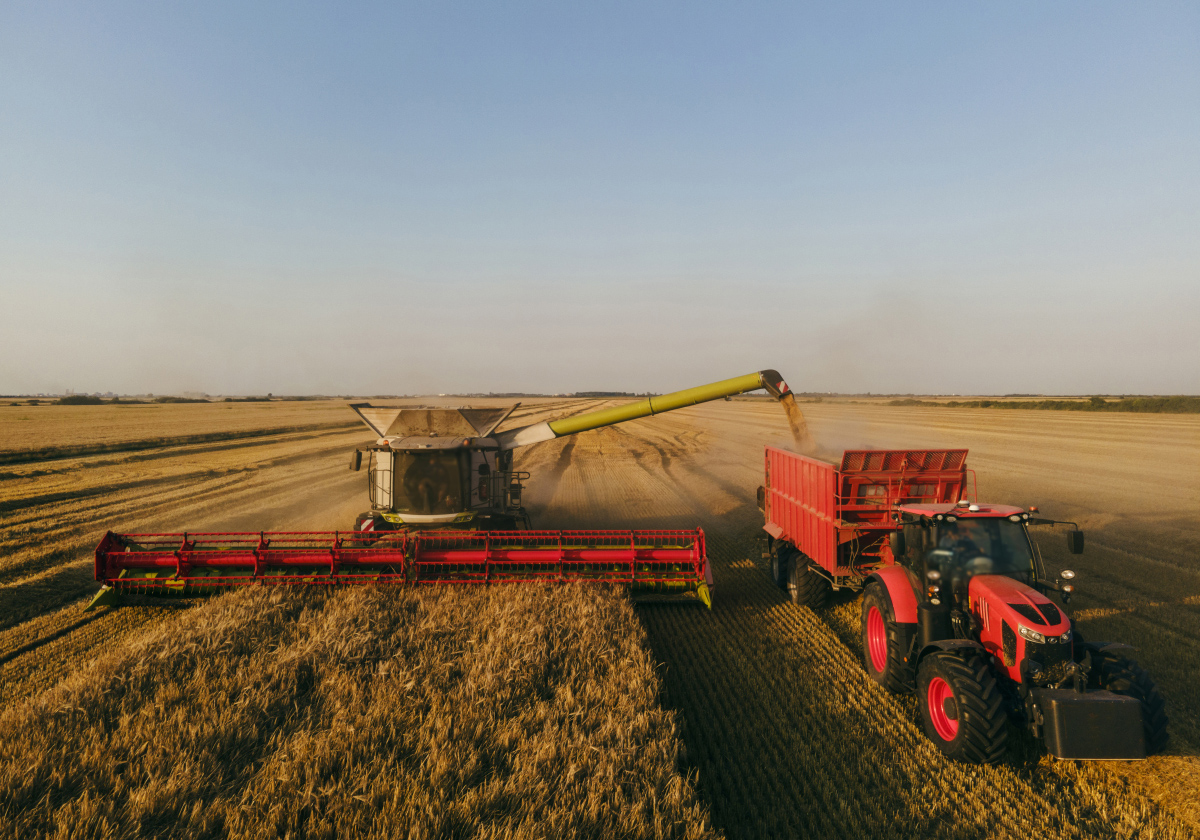

2. Working Components
Working components in agricultural machinery, such as tillage and harvesting tools, are subjected to high stresses and wear. Castings are ideal for producing complex shapes and larger parts, such as plow bodies and harrow blades, while offering good wear resistance. Forgings are used for cutting tools and other parts that encounter high impact forces, providing superior strength and durability for long-term operation in harsh field conditions.
· Castings: Plow bodies, Harrow blades, Cultivator tines
· Forgings: Cutting blades, Chisels, Tiller tines
3. Frame and Structural Components
The frame and structural components support the entire machinery and ensure its stability during operation. Castings are typically used for parts like machine bases and brackets, where complex shapes and cost-effective mass production are required. Forgings are used for high-strength structural components such as reinforced arms, beams, and axles, which must resist deformation and provide stability under heavy loads.
· Castings: Machine base, Chassis, Support brackets
· Forgings: Reinforced arms, Structural beams, Axles
4. Hydraulic System Components
Hydraulic systems are crucial for controlling attachments and providing power to various implements in agricultural machinery. Castings are used for manufacturing complex housings like hydraulic pump bodies and valve bodies, which need precision and durability. Forged components, such as hydraulic pistons and rods, are essential for handling high-pressure loads and providing strength and longevity in demanding conditions.
· Castings: Hydraulic pump housing, Valve body, Oil tank
· Forgings: Hydraulic piston, Hydraulic rod, Connecting rod
5. Chassis and Wheel Systems
The chassis and wheel systems bear the weight of the machine and enable it to move across different terrains. Castings are used for producing large components such as wheels, hubs, and suspension parts, offering durability and ease of production. Forged parts like axles, wheel shafts, and wheel bearings are used in critical load-bearing applications, ensuring the strength and long-term reliability of the vehicle's movement.
· Castings: Wheels, Wheel hubs, Suspension components
· Forgings: Axles, Wheel shafts, Connecting rods
6. Powertrain and Drive Components
Powertrain and drive components are essential for the transmission of power from the engine to the wheels or other parts of the machinery. Castings are used for producing housing components that enclose the gears and shafts, while forgings are used for high-strength components like gears, drive shafts, and splines, which need to withstand high levels of torque and dynamic stress, ensuring the machinery's operational efficiency.
· Castings: Drive housing, Gearbox housing, Differential case
· Forgings: Crankshaft, Drive shaft, Gears, Differential gears
7. Steering and Control Systems
Steering and control systems are vital for maneuvering agricultural machinery efficiently. Castings are used to create intricate components like steering gear housings and control levers, offering ease of production and precision. Forgings are applied to parts like steering shafts and linkages, which must endure heavy loads and frequent movement, ensuring smooth and reliable control for the operator.
· Castings: Steering gear housing, Control levers, Steering column
· Forgings: Steering shaft, Linkages, Ball joints
Available Materials For Agricultural Machinery Parts
Cast Iron
In agricultural machinery, cast iron and its derivatives are manufactured into various parts through sand casting, lost foam casting, and heat treatment.
·Gray cast iron
Gray cast iron has excellent vibration absorption properties and is used in engine blocks, gearbox housings, and brake discs to reduce operating vibration and ensure stability.
·Ductile iron
Ductile iron, with its high strength and toughness, is suitable for manufacturing wheel hubs, bogie components, gears, and bearing seats through sand or lost foam casting, capable of withstanding impact and fatigue loads.
·Compacted graphite iron
Compacted graphite iron combines vibration absorption with strength and is used in hydraulic chassis components and long-term load-bearing structural parts.
·Alloy cast iron
Alloy cast iron is wear-resistant and heat-resistant. Through temperature-controlled casting or alloying, it is used in tillage machinery blade shafts, grinder bushings, and high-friction components. Some parts can be enhanced through localized heat treatment or machining.
Steel
In agricultural machinery, steel is used to manufacture various load-bearing components through forging, casting, heat treatment, and precision machining.
·Carbon steel
Carbon steel, with its high strength and toughness, is forged for impact-bearing parts such as drive shafts, connecting rods, wheel axles, and tiller blade carriers.
·Low-alloy steel
Low-alloy steel, with its superior wear and fatigue resistance, is forged for gears, hydraulic pump housings, and high-stress connectors.
·Cast steel
Cast steel, with its excellent formability, is cast for hydraulic cylinders, transmission housings, and large chassis components, ensuring dimensional accuracy and mechanical properties.
·High-manganese steel
High-manganese steel, with its wear and impact resistance, is cast and heat-treated for tillage blades, track shoes, roller shafts, and crusher rollers, adapting to heavy loads and impact conditions.
Aluminum Alloy
In agricultural machinery, aluminum alloys are used to create lightweight parts through die casting, sand casting, extrusion, and machining.
·High-strength aluminum alloys
High-strength aluminum alloys, with their light weight and high specific strength, are used in cab skins, engine hoods, and lightweight brackets through die casting or extrusion, reducing overall machine weight while maintaining structural strength.
·Corrosion-resistant aluminum alloys
Corrosion-resistant aluminum alloys can form a dense oxide film on their surfaces, which can be used through precision casting or machining to create hydraulic guides, decorative parts, and fasteners, enhancing durability.
·Easy-to-machine aluminum alloys
Easy-to-machine aluminum alloys are easy to machine and weld, making them suitable for instrument brackets, protective covers, and electrical equipment housings. Heat treatment can be used to optimize strength and toughness.
Other Metal Alloys
In addition to common cast iron, steel, and aluminum, agricultural machinery also utilizes specialty metals such as copper, titanium, magnesium, molybdenum, and tungsten. These alloys are typically selected for their heat resistance, corrosion resistance, or high strength.
·Copper and copper alloys
They offer wear resistance and excellent electrical conductivity. They are used in electrical components, bearing bushings, and hydraulic slides through casting or machining.
·Titanium alloys
They offer high strength, light weight, and corrosion resistance, making them suitable for forging or machining into high-performance springs, fasteners, and structural brackets.
·Magnesium alloys
They offer low density and excellent machinability. They are used in cab skins, brackets, and instrument panels through die casting and machining, reducing overall machine weight.
Cast Iron
In agricultural machinery, cast iron and its derivatives are manufactured into various parts through sand casting, lost foam casting, and heat treatment.
·Gray cast iron
Gray cast iron has excellent vibration absorption properties and is used in engine blocks, gearbox housings, and brake discs to reduce operating vibration and ensure stability.
·Ductile iron
Ductile iron, with its high strength and toughness, is suitable for manufacturing wheel hubs, bogie components, gears, and bearing seats through sand or lost foam casting, capable of withstanding impact and fatigue loads.
·Compacted graphite iron
Compacted graphite iron combines vibration absorption with strength and is used in hydraulic chassis components and long-term load-bearing structural parts.
·Alloy cast iron
Alloy cast iron is wear-resistant and heat-resistant. Through temperature-controlled casting or alloying, it is used in tillage machinery blade shafts, grinder bushings, and high-friction components. Some parts can be enhanced through localized heat treatment or machining.
Steel
In agricultural machinery, steel is used to manufacture various load-bearing components through forging, casting, heat treatment, and precision machining.
·Carbon steel
Carbon steel, with its high strength and toughness, is forged for impact-bearing parts such as drive shafts, connecting rods, wheel axles, and tiller blade carriers.
·Low-alloy steel
Low-alloy steel, with its superior wear and fatigue resistance, is forged for gears, hydraulic pump housings, and high-stress connectors.
·Cast steel
Cast steel, with its excellent formability, is cast for hydraulic cylinders, transmission housings, and large chassis components, ensuring dimensional accuracy and mechanical properties.
·High-manganese steel
High-manganese steel, with its wear and impact resistance, is cast and heat-treated for tillage blades, track shoes, roller shafts, and crusher rollers, adapting to heavy loads and impact conditions.
Aluminum Alloy
In agricultural machinery, aluminum alloys are used to create lightweight parts through die casting, sand casting, extrusion, and machining.
·High-strength aluminum alloys
High-strength aluminum alloys, with their light weight and high specific strength, are used in cab skins, engine hoods, and lightweight brackets through die casting or extrusion, reducing overall machine weight while maintaining structural strength.
·Corrosion-resistant aluminum alloys
Corrosion-resistant aluminum alloys can form a dense oxide film on their surfaces, which can be used through precision casting or machining to create hydraulic guides, decorative parts, and fasteners, enhancing durability.
·Easy-to-machine aluminum alloys
Easy-to-machine aluminum alloys are easy to machine and weld, making them suitable for instrument brackets, protective covers, and electrical equipment housings. Heat treatment can be used to optimize strength and toughness.
Other Metal Alloys
In addition to common cast iron, steel, and aluminum, agricultural machinery also utilizes specialty metals such as copper, titanium, magnesium, molybdenum, and tungsten. These alloys are typically selected for their heat resistance, corrosion resistance, or high strength.
·Copper and copper alloys
They offer wear resistance and excellent electrical conductivity. They are used in electrical components, bearing bushings, and hydraulic slides through casting or machining.
·Titanium alloys
They offer high strength, light weight, and corrosion resistance, making them suitable for forging or machining into high-performance springs, fasteners, and structural brackets.
·Magnesium alloys
They offer low density and excellent machinability. They are used in cab skins, brackets, and instrument panels through die casting and machining, reducing overall machine weight.
How To Customize Agricultural Machinery Parts
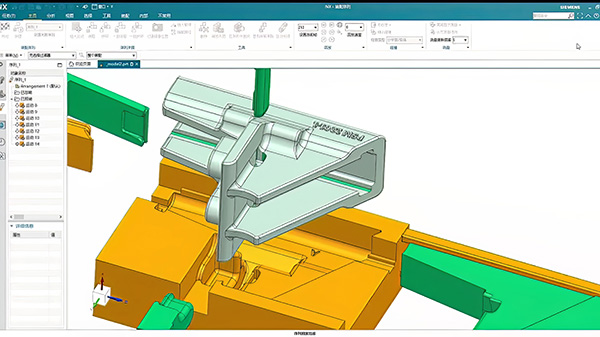
3D Drawings
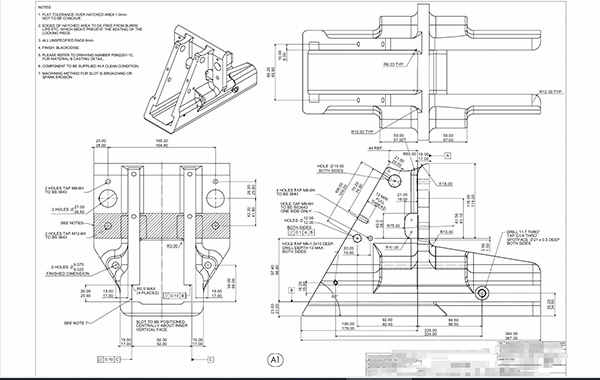
Processing Drawings

Sample
1. Provide Detailed Design Documents Or Samples
2. Confirm Material/Process/Performance
3. Make molds and samples
4. Comprehensive Sample Inspection
5. Mass Production
6. Post-production Parts Multiple Quality Inspections
1. Provide Detailed Design Documents Or Samples
2. Confirm Material/Process/Performance
3. Make molds and samples
4. Comprehensive Sample Inspection
5. Mass Production
6. Post-production Parts Multiple Quality Inspections
Custom Processing Of Agricultural Machinery Parts

Casting
In the agricultural machinery parts industry, casting processes are used to produce parts with complex shapes and sizes, such as agricultural machinery engine blocks, gearbox housings and pump housings. They are suitable for manufacturing large and complex parts that require high strength and durability, so that the parts can withstand the heavy loads, vibrations and harsh operating conditions common in agricultural machinery.

Forging
In the field of agricultural machinery parts, forging processes are used to produce high-strength components such as axles, gears, shafts and structural parts, improving the mechanical strength and reliability of equipment (such as harvesters, plows and tractors) that operate under heavy loads and continuous use.
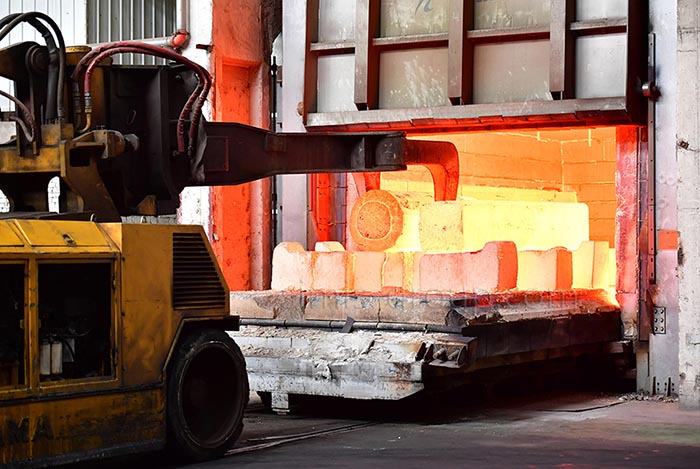

Heat Treatment
In the manufacturing of agricultural machinery parts, heat treatment is applied to connecting transmission components such as gears, shafts and bearings, which can improve the wear resistance and toughness of high-friction and high-stress components, extend the service life of mechanical parts and reduce maintenance requirements.

Machining
In the agricultural machinery parts industry, machining is used to produce precision components such as engine parts, hydraulic accessories and transmission system components, ensuring proper fit and clearance of parts, thereby improving the performance, efficiency and service life of agricultural machinery such as tractors, tillers and combine harvesters.

Sheet Metal Fabrication
In the agricultural machinery parts industry, sheet metal fabrication processes are used to produce components such as chassis, frames, guards and body panels. Sheet metal fabrication is able to produce lightweight but high-strength components that improve the overall structural integrity and safety of agricultural equipment, while also being able to efficiently produce a large number of components with varying designs.

Surface Treatment
In the manufacturing of agricultural machinery parts, surface treatment is used on components such as plow blades, harvester knives and frames through processes such as coating, electroplating and anodizing to improve corrosion resistance, wear resistance and durability, helping to protect parts from harsh environmental conditions such as moisture, dirt and chemicals, ensuring reliable performance and extending the service life of key agricultural machinery components.





























