Custom Metal Parts For Rail Train
Customized railway train metal components are designed and manufactured according to the specific needs of the railway industry, including brake systems, wheels, axles, couplings and structural parts, track parts and other components. These parts are usually made of high-strength materials such as steel or iron. Through precise drawing design and customized manufacturing processes, the durability, wear resistance and corrosion resistance of the components can be ensured, as well as the ability to withstand extreme operating conditions such as heavy loads, high speeds and changing weather environments.
Rail Train Parts Classification
1. Wheel and Axle Assembly
The wheel and axle assembly is a critical component for the stability and movement of rail trains, providing both support and traction. Castings are typically used for wheel hubs and axle housings due to their complex shapes and structural integrity. Forgings are employed for axles and wheels to ensure strength, durability, and resistance to fatigue under heavy loads and constant use.
· Castings: Wheel hubs, Axle housings
· Forgings: Train wheels, Axles
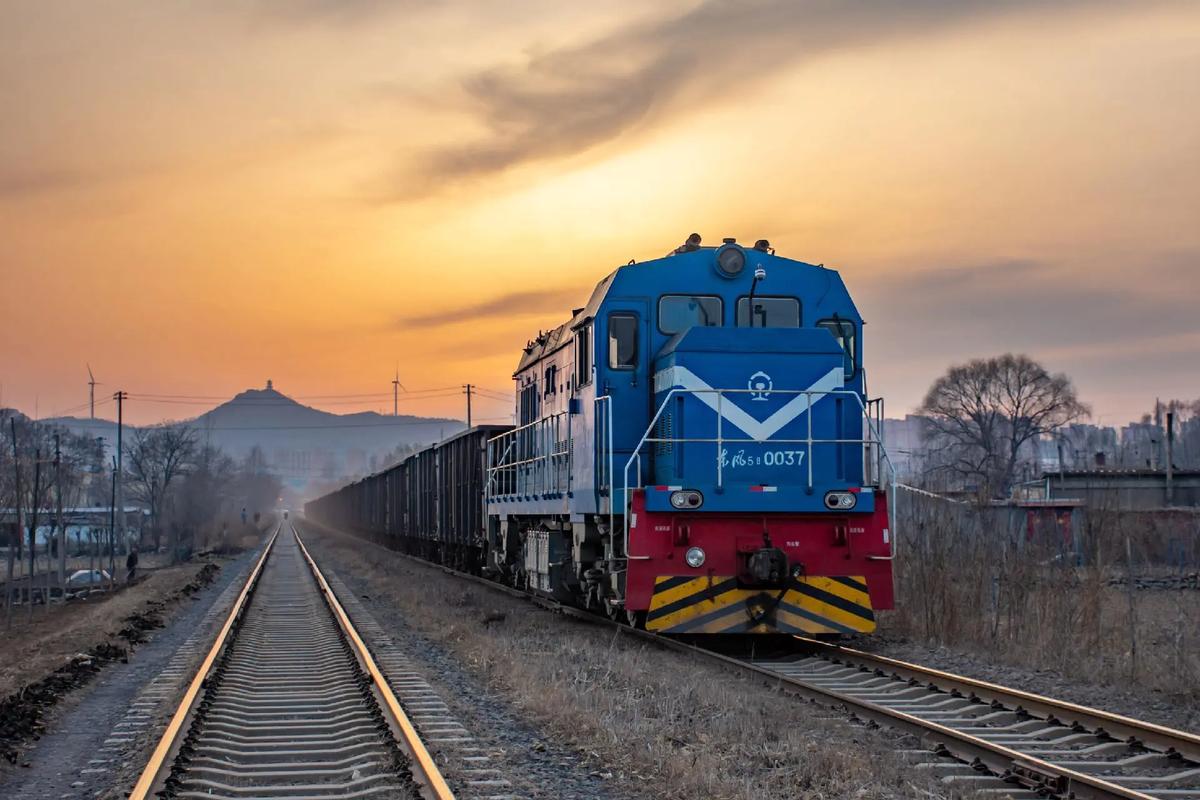

2. Brake System
The brake system ensures the safe stopping and control of the train, especially under high-speed or heavy-load conditions. Castings are often used for brake components like calipers or housings, which require intricate shapes and high strength. Forgings are used for critical components such as brake discs or pistons, where high wear resistance and mechanical strength are essential.
· Castings: Brake calipers, Brake housings
· Forgings: Brake discs, Brake pistons
3. Coupling System
The coupling system connects multiple carriages of a train, transferring power and ensuring structural integrity during movement. Castings are used for coupling housings, while forgings are necessary for the main coupler components, which must withstand high forces and provide long-term reliability under dynamic conditions.
· Castings: Coupling housings
· Forgings: Couplers, Coupling pins
4. Suspension System
The suspension system supports the weight of the train and absorbs vibrations from the track, ensuring smooth operation. Castings are typically used for suspension brackets or housings, whereas forgings are employed for components like suspension springs or leaf spring brackets that experience high loads and stresses.
· Castings: Suspension brackets, Housings
· Forgings: Suspension springs, Leaf spring brackets
5. Frame and Chassis
The frame and chassis form the structural foundation of the rail train, providing the necessary strength and rigidity to support all other components. Castings are used for complex frame components, while forgings are used for critical load-bearing parts like cross members, ensuring robustness under extreme stresses.
· Castings: Frame components, Support brackets
· Forgings: Cross members, Chassis components
6. Engine Components
Engine components are responsible for generating the power necessary for train operation. Castings are used for engine blocks and various housings, while forgings are used for components such as crankshafts and connecting rods that must withstand high levels of stress, heat, and wear over time.
· Castings: Engine block, Oil pan
· Forgings: Crankshaft, Connecting rods
7. Railway Track Components
Railway track components include elements that ensure secure rail fastening and proper alignment. Castings are used for rail chairs, baseplates, and fishplates, which are subject to complex loading conditions. Forgings are utilized for components like rail clips and fasteners that need to provide high strength and maintain tight tolerances.
· Castings: Rail chairs, Baseplates, Fishplates
· Forgings: Rail clips, Track fasteners
Available Materials For Rail Train Parts
Cast Iron
In railway vehicles and track systems, cast iron and its derivatives are processed into various castings through sand casting, lost foam casting, and heat treatment.
·Gray cast iron
Gray cast iron offers excellent vibration absorption properties and is used in components such as brake discs and gearbox housings to reduce operating noise.
·Ductile iron
Ductile iron, with its high strength and toughness, is formed through sand or lost foam casting and is suitable for parts subject to impact and fatigue, such as wheel centers, bogie components, and coupler dampers.
·Compacted graphite iron
Compacted graphite iron combines vibration absorption and strength and is used in complex chassis components and long-duration load-bearing structural parts.
·Alloy cast iron
Alloy cast iron is wear-resistant and heat-resistant. Through temperature-controlled casting or alloying, it is used in high-friction or high-temperature components such as brake shoes and diesel engine cylinder liners. Some parts can also be combined with partial forging or heat treatment to further enhance performance.
Steel
Steel is manufactured into various parts in the railway industry through casting, forging, and heat treatment.
·Carbon steel
Carbon steel offers high strength and toughness, and forging ensures continuous fiber flow. It is used in impact-bearing components such as axles, couplers, and couplers.
·Low-alloy steel
Low-alloy steel exhibits excellent wear and fatigue resistance, making it suitable for bogie components and high-stress connections after forging.
·Cast steel
Cast steel offers excellent formability, and the casting process can meet the dimensional accuracy requirements of large, complex structural components such as bogie sideframes, bolsters, and buffer housings.
·High-manganese steel
High-manganese steel is wear- and impact-resistant. Through casting and solution treatment, it is used in turnout rails, frogs, and rail joints, meeting heavy load and high-speed operating conditions.
·Weathering steel
Weathering steel is corrosion-resistant and suitable for car body panels and bridge components, reducing maintenance frequency.
·Stainless steel
Stainless steel offers excellent corrosion and heat resistance and is used in brake discs, bolts, and fasteners, ensuring long-term and stable operation.
Aluminum Alloy
In railway vehicles and track systems, aluminum alloys are manufactured into various parts through die casting, sand casting, heat treatment, and precision machining.
·High-strength aluminum alloys
High-strength aluminum alloys, with their light weight and high specific strength, are used in vehicle body panels, door and window frames, and seat structures through die casting or extrusion, reducing vehicle weight while maintaining structural strength.
·Corrosion-resistant aluminum alloys
Corrosion-resistant aluminum alloys can form a dense oxide film on their surfaces, which can be precision-cast or machined into brake guides, decorative parts, and fasteners, enhancing component durability and service life.
·Machinable aluminum alloys
Machinable aluminum alloys are easy to machine and weld, making them suitable for complex shapes such as end caps, shrouds, and electrical equipment housings. Heat treatment optimizes strength and toughness, ensuring long-term, stable operation.
Other Metal Alloys
In addition to common materials such as cast iron, steel, and aluminum, other specialty alloys are used in rail and train vehicle components. These alloys are often selected for their exceptional properties, such as heat resistance, corrosion resistance, or high strength, for specific applications requiring extreme performance.
·Copper alloys
Copper and copper alloys are cast and machined into conductive and wear-resistant parts. Red copper, with its excellent conductivity and wear resistance, is used in components such as electrical busbars, contactors, and slip rings, ensuring stable operation of electrical systems. Bronze and lead bronze are wear-resistant and anti-friction, and are cast and precision-machined into bearings, bushings, brake guides, and gear sleeves, extending component life.
·Titanium alloys
Titanium alloys offer high strength, light weight, and corrosion resistance, making them suitable for forging or precision machining vehicle body components, springs, fasteners, and high-performance mechanical parts, enhancing overall efficiency and durability in high-speed trains or special-duty vehicles.
·Magnesium alloys
Magnesium alloys, with their low density and excellent machinability, can be die-cast and machined into vehicle body panels, interior brackets, and instrument panels, significantly reducing vehicle weight.
Cast Iron
In railway vehicles and track systems, cast iron and its derivatives are processed into various castings through sand casting, lost foam casting, and heat treatment.
·Gray cast iron
Gray cast iron offers excellent vibration absorption properties and is used in components such as brake discs and gearbox housings to reduce operating noise.
·Ductile iron
Ductile iron, with its high strength and toughness, is formed through sand or lost foam casting and is suitable for parts subject to impact and fatigue, such as wheel centers, bogie components, and coupler dampers.
·Compacted graphite iron
Compacted graphite iron combines vibration absorption and strength and is used in complex chassis components and long-duration load-bearing structural parts.
·Alloy cast iron
Alloy cast iron is wear-resistant and heat-resistant. Through temperature-controlled casting or alloying, it is used in high-friction or high-temperature components such as brake shoes and diesel engine cylinder liners. Some parts can also be combined with partial forging or heat treatment to further enhance performance.
Steel
Steel is manufactured into various parts in the railway industry through casting, forging, and heat treatment.
·Carbon steel
Carbon steel offers high strength and toughness, and forging ensures continuous fiber flow. It is used in impact-bearing components such as axles, couplers, and couplers.
·Low-alloy steel
Low-alloy steel exhibits excellent wear and fatigue resistance, making it suitable for bogie components and high-stress connections after forging.
·Cast steel
Cast steel offers excellent formability, and the casting process can meet the dimensional accuracy requirements of large, complex structural components such as bogie sideframes, bolsters, and buffer housings.
·High-manganese steel
High-manganese steel is wear- and impact-resistant. Through casting and solution treatment, it is used in turnout rails, frogs, and rail joints, meeting heavy load and high-speed operating conditions.
·Weathering steel
Weathering steel is corrosion-resistant and suitable for car body panels and bridge components, reducing maintenance frequency.
·Stainless steel
Stainless steel offers excellent corrosion and heat resistance and is used in brake discs, bolts, and fasteners, ensuring long-term and stable operation.
Aluminum Alloy
In railway vehicles and track systems, aluminum alloys are manufactured into various parts through die casting, sand casting, heat treatment, and precision machining.
·High-strength aluminum alloys
High-strength aluminum alloys, with their light weight and high specific strength, are used in vehicle body panels, door and window frames, and seat structures through die casting or extrusion, reducing vehicle weight while maintaining structural strength.
·Corrosion-resistant aluminum alloys
Corrosion-resistant aluminum alloys can form a dense oxide film on their surfaces, which can be precision-cast or machined into brake guides, decorative parts, and fasteners, enhancing component durability and service life.
·Machinable aluminum alloys
Machinable aluminum alloys are easy to machine and weld, making them suitable for complex shapes such as end caps, shrouds, and electrical equipment housings. Heat treatment optimizes strength and toughness, ensuring long-term, stable operation.
Other Metal Alloys
In addition to common materials such as cast iron, steel, and aluminum, other specialty alloys are used in rail and train vehicle components. These alloys are often selected for their exceptional properties, such as heat resistance, corrosion resistance, or high strength, for specific applications requiring extreme performance.
·Copper alloys
Copper and copper alloys are cast and machined into conductive and wear-resistant parts. Red copper, with its excellent conductivity and wear resistance, is used in components such as electrical busbars, contactors, and slip rings, ensuring stable operation of electrical systems. Bronze and lead bronze are wear-resistant and anti-friction, and are cast and precision-machined into bearings, bushings, brake guides, and gear sleeves, extending component life.
·Titanium alloys
Titanium alloys offer high strength, light weight, and corrosion resistance, making them suitable for forging or precision machining vehicle body components, springs, fasteners, and high-performance mechanical parts, enhancing overall efficiency and durability in high-speed trains or special-duty vehicles.
·Magnesium alloys
Magnesium alloys, with their low density and excellent machinability, can be die-cast and machined into vehicle body panels, interior brackets, and instrument panels, significantly reducing vehicle weight.
How To Customize Rail Train Parts
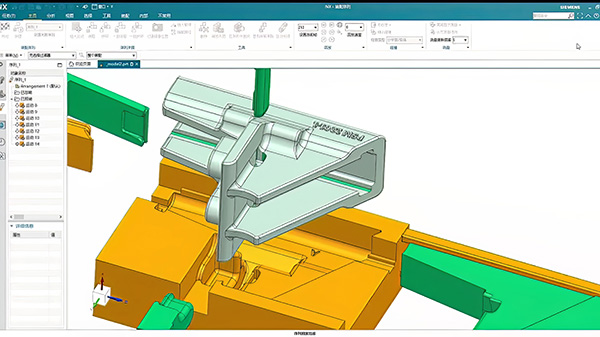
3D Drawings
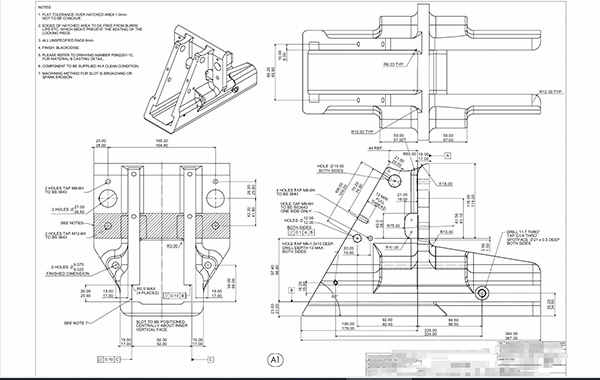
Processing Drawings
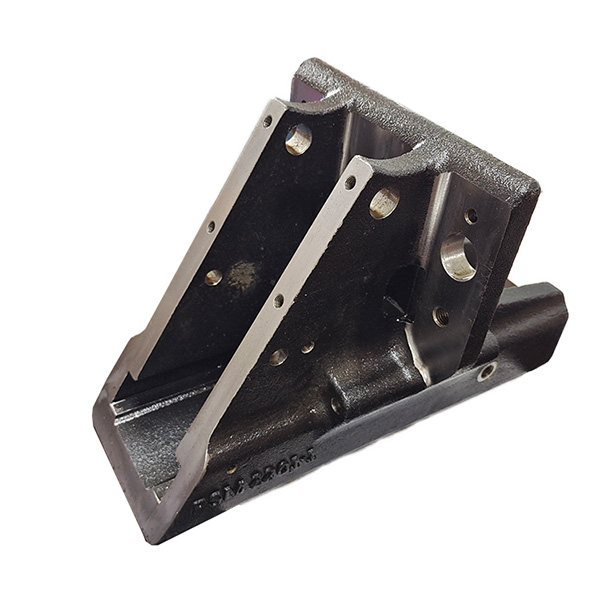

Sample
1. Provide Detailed Design Documents Or Samples
2. Confirm Material/Process/Performance
3. Make Production Molds And Samples
4. Comprehensive Sample Inspection
5. Mass Production
6. Post-production Parts Multiple Quality Inspections
1. Provide Detailed Design Documents Or Samples
2. Confirm Material/Process/Performance
3. Make Production Molds And Samples
4. Comprehensive Sample Inspection
5. Mass Production
6. Post-production Parts Multiple Quality Inspections
Custom Processing of Rail Train Parts

Casting
In the railway train parts industry, casting processes are used to produce metal critical components of various complex shapes and sizes such as train wheels, brake housings and engine blocks. These parts require high structural integrity and durability to withstand the heavy loads, vibrations and environmental conditions common in railway systems.

Forging
In the field of railway train components, forging processes are used to produce high-strength components such as axles, suspension components and coupling mechanisms. These forged components have excellent fatigue resistance and mechanical strength, ensuring the safety, reliability and service life of the train system under extreme operating conditions.
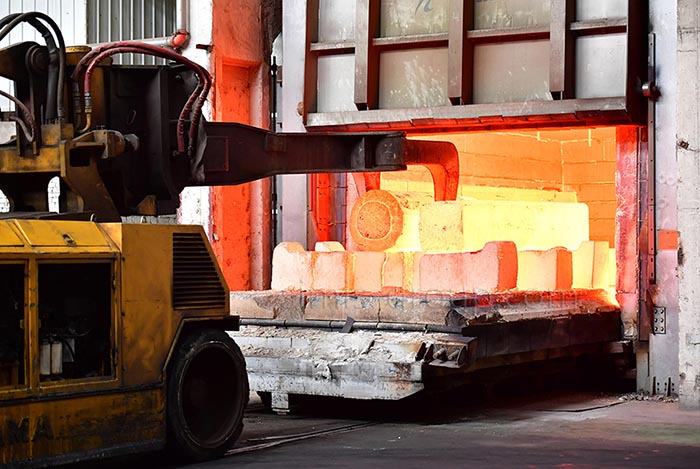

Heat Treatment
In the railway train parts industry, heat treatment is used to improve the mechanical properties of components such as train wheels, rails and axles, and to increase the wear resistance, toughness and fatigue strength of parts, especially those used in railway transportation systems that are exposed to continuous friction, high pressure and thermal cycles.
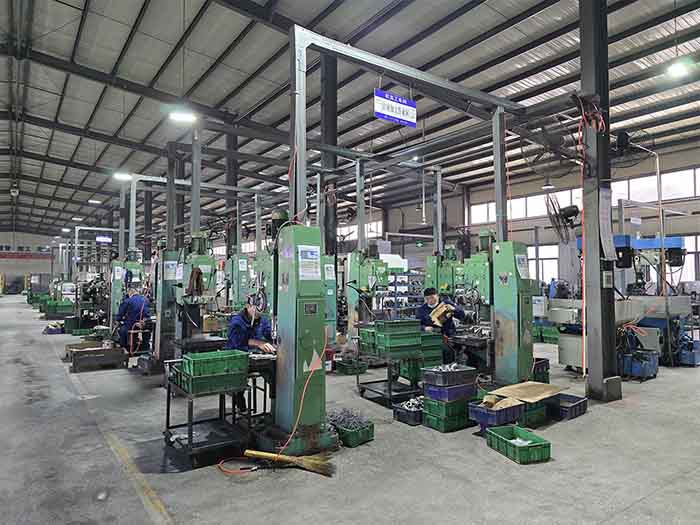

Machining
In the railway train parts industry, machining ensures that critical components such as engine parts, bearing seats and gears meet strict tolerances and quality standards, ensuring that railway systems operate safely and efficiently.

Sheet Metal Fabrication
In the field of railway train components, sheet metal processing is used to manufacture parts such as train body panels, internal frames and safety shields. Sheet metal processing provides lightweight, durable components that improve the overall structural integrity, safety and performance of the train.

Surface Treatment
In the railway train components industry, surface treatment processes such as galvanizing, anodizing and coating are used to protect components from corrosion, wear and environmental damage. Train components such as wheels, axles and brake systems are often surface treated to improve their durability, reduce maintenance and extend the life of critical components that operate under harsh operating conditions.













