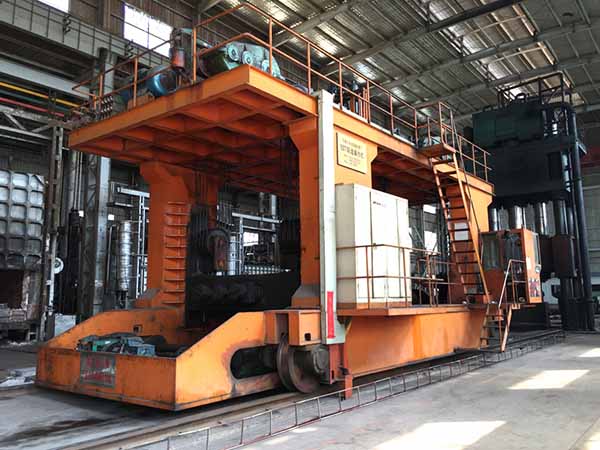
Simis Open-die Forging Factory
Simis Open-die Forging Factory Introduction
Simis Open-die Forging Factory has high forging flexibility and can produce various types of forgings (rings, shafts, flanges, gears, etc.) from small parts to large structural parts with complex shapes. It can forge carbon steel, alloy steel, stainless steel, aluminum alloy, copper alloy and other metal alloy materials for automotive, industrial, energy, mining, shipbuilding and other industries.
Simis Open-die Forging Factory advanced forging equipment, including large forging hammers and hydraulic presses, which can handle heavy workpieces from tens of kilograms to several tons. The factory also has a complete temperature control system to ensure uniform heating of the metal during the forging process, reduce deformation stress and improve the mechanical properties of the forgings.
Open-die Forging Process
Open-die forging process overview:
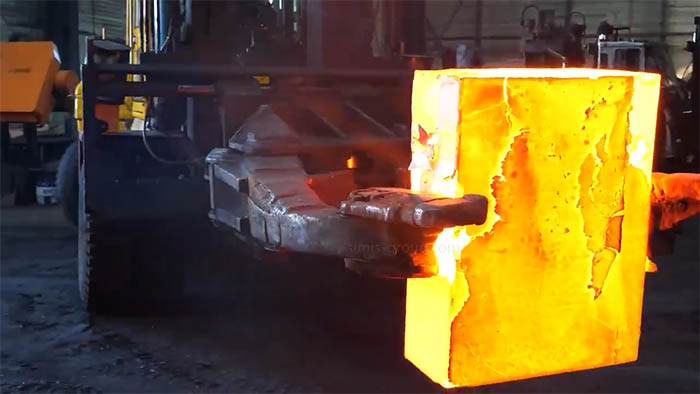
Open-die forging is a metalworking process where heated metal billets are shaped under repeated hammer blows or pressure without being fully confined within a die. Open-die forging process allows for greater flexibility in forging large or customized parts while improving the metal's mechanical properties.
1. Material selection and preparation
Select the appropriate metal material according to the required mechanical properties of the part, cut it into billets of specified size or weight, and remove contaminants, rust or oxide layers from the billets.
2. Heating the billet
The metal billet is uniformly heated to a specified temperature in a furnace to increase its deformation plasticity.
3. Forging operation
The heated metal billet is placed on a flat or slightly contoured die and deformed using controlled blows of a hammer or press. The shape of the part is forged through operations such as upsetting, stretching (elongation), bending, punching, twisting, and flattening (the workpiece is not constrained in the transverse direction and can be flexibly formed).
· Upsetting: used to shorten the length of the blank, increase the cross-sectional area, make it closer to the final shape, and improve the material organization.
· Drawing Out: Increase the length of the blank and reduce the cross-section, mainly used in the manufacture of shaft and rod parts.
· Punching: Increase the length of the blank and reduce the cross-section, mainly used in the manufacture of shaft and rod parts.
· Punching: Use a punch to apply pressure on the blank to form a hole, used to make annular or perforated parts.
· Reaming: Expand the workpiece after punching to obtain a larger inner diameter and uniform wall thickness.
· Bending: Bend the blank into the desired shape, suitable for the manufacture of hook-shaped, elbow and other parts.
· Twisting: Rotate the blank around the axis at a certain angle, suitable for parts that require a specific twisted shape.
4. Cooling
The forged parts are gradually cooled to minimize internal stress and prevent cracking.
Some forged parts can be directly transferred to the heat treatment step to enhance performance.
5. Heat treatment
Forgings are heat treated by normalizing, annealing, quenching, and tempering to improve the mechanical properties of forgings, release internal stress, and refine the grain structure.
6. Quality Inspection
Strictly inspect and correct the size, shape and performance of forgings to ensure that the products meet the design requirements.
7. Finishing and Final Processing
Surface treatment and subsequent processing of forgings are carried out according to customer requirements.
8. Quality Inspection
Comprehensive measurement is carried out through surface quality inspection, dimension inspection, mechanical property test and other quality inspection methods to ensure that the forgings meet the requirements of the design drawings.



Materials Of Open-die Forging
What metal parts can be forged in Simis Open-die Forging Factory?
The SIMIS open die forging plant can forge a variety of metal materials, including carbon steel, alloy steel, and stainless steel, each with varying mechanical properties and corrosion resistance. Through multi-directional deformation using hammering or a press on a flat anvil, it produces large shafts, rings, and blocks. These materials feature continuous grain flow and high internal density, making them suitable for heavy-duty, large-scale critical components. The SIMIS open die forging plant can produce high-strength, high-toughness, and complex-shaped metal forgings, widely used in the automotive, energy, mining, shipbuilding, and heavy machinery sectors.
Carbon Steel Open Die Forging
Used for shafts, rolls, crankshafts, and connecting rods. Post-forging normalizing or quenching and tempering improves overall mechanical properties.
Common metal grades: ASTM A105, A350 LF2, AISI 1045, and 4140.
Alloy Steel Open Die Forging
Used for large gear blanks, bushings, and connecting shafts. Post-forging quenching and tempering or case hardening improves strength, toughness, and wear resistance.
Common metal grades: AISI 4140, 4340, 8630, 52100.
Stainless Steel Open Die Forging
Suitable for corrosion-resistant and high-temperature shafts, such as those for chemical equipment and fans. Post-forging solution treatment or stabilization treatment enhances corrosion resistance.
Common metal grades: ASTM A182 F304, F316, F321, and F51.
































