Custom Metal Parts For Electrical & Lighting
Custom metal parts for electrical equipment and lighting are usually made of high-performance materials such as aluminum, steel and copper alloys, which have good conductivity, corrosion resistance and structural integrity, ensuring efficient energy transmission, protecting electrical components from environmental conditions and providing long-lasting performance in applications such as street lighting, industrial lighting and electrical infrastructure. These parts are customized for optimal performance, reliability and cost-effectiveness in the electrical and lighting industry through custom manufacturing technologies such as casting, forging and machining.
Electrical & Lighting Parts Classification
1.Lighting Fixtures
Lighting fixtures require precision and durability to withstand the demands of both residential and industrial environments. Castings are frequently used for the intricate housings and bases of lighting fixtures, ensuring structural stability and aesthetic design. Forgings are used for high-strength components like lamp posts and mounting brackets, where resistance to external stresses and long-term performance are critical.
· Castings: Lighting housings, Lamp bases, Reflector assemblies
· Forgings: Lamp posts, Mounting brackets, Structural supports

2.Electrical Enclosures
Electrical enclosures house and protect critical electrical components, such as circuit breakers, switches, and control panels. Castings are used to form the intricate shapes and complex geometries of enclosures that require a robust structure and protection from environmental factors. Forgings are used for parts that need to handle dynamic loads and ensure secure, reliable electrical connections, such as terminal blocks and busbar supports.
· Castings: Enclosure housings, Junction box covers, Panel bases
· Forgings: Terminal blocks, Busbar supports, Switchgear components
3.Switchgear and Circuit Protection
Switchgear and circuit protection systems are designed to control and protect electrical circuits from overloads and faults. Castings are typically used for the housing and structural components, providing effective heat dissipation and protection. Forgings are essential for high-strength parts such as circuit breaker contacts, busbars, and connectors, ensuring reliability in high-voltage applications and minimizing wear and tear.
· Castings: Circuit breaker housings, Distribution board enclosures, Fuse holders
· Forgings: Circuit breaker contacts, Busbars, Disconnect switches
4.Connectors and Terminals
Electrical connectors and terminals are crucial for ensuring secure and reliable connections in wiring systems. Castings are often used for producing intricate shapes for connector housings and terminals with specific electrical and mechanical properties. Forgings are used for high-precision connectors and terminals that need to endure high electrical currents, such as power distribution connectors and grounding terminals.
· Castings: Connector housings, Terminal blocks, Cable connectors
· Forgings: Power connectors, Pin connectors, Grounding terminals
5.Power Distribution Components
Power distribution systems rely on durable components to safely deliver electrical power from the source to end-users. Castings are used for components like distribution transformers and busbar enclosures, which need to house electrical equipment and ensure efficient operation. Forgings are used for parts like bushings, power connectors, and heavy-duty mounting brackets, which must handle large currents and mechanical stresses.
· Castings: Transformer housings, Busbar enclosures, Distribution boxes
· Forgings: Bushing assemblies, Power connectors, Mounting brackets
6.Electrical Motor Components
Motors used in electrical systems require parts that can endure high rotational speeds, mechanical stresses, and thermal cycling. Castings are often used for motor housings, bearing seats, and other structural components that need intricate shapes and strong structural integrity. Forgings are employed for high-strength, high-performance parts such as rotor shafts, bearings, and gears, where precise tolerances and resistance to fatigue are critical.
· Castings: Motor housings, Bearing seats, End bells
· Forgings: Rotor shafts, Bearing races, Gears
7.Street and Industrial Lighting Poles
Street lighting poles are designed to endure outdoor weather conditions while providing a safe and stable base for lighting fixtures. Castings are used for base components and decorative elements, providing excellent corrosion resistance and ease of manufacturing. Forgings are used for high-strength mounting and support arms that ensure the stability of the lighting poles under heavy wind loads and other dynamic forces.
· Castings: Pole bases, Decorative elements, Mounting rings
· Forgings: Support arms, Mounting brackets, Reinforced connectors
Available Materials For Electrical & Lighting Parts
Cast Iron
In the electrical equipment and lighting industries, cast iron is used to manufacture housings and supporting components with high rigidity and excellent vibration absorption. Sand casting, lost foam casting, and subsequent machining are often used to achieve complex shapes and stable dimensions.
·Gray Cast Iron
Gray cast iron is often sand-casted to form motor bases, transformer housings, and equipment support frames. It offers excellent vibration absorption, reducing operating noise and mechanical vibration.
·Ductile Iron
Ductile iron, achieved through sand casting and heat treatment, achieves high strength and toughness. It is suitable for switchgear brackets, distribution box bases, and high-strength mounting brackets, ensuring stability under operating conditions such as opening and closing and vibration.
·Compacted Graphite Iron
Compacted graphite iron offers a balance of strength and vibration absorption, making it suitable for large motor housings and generator bases. Temperature-controlled casting ensures uniform microstructure, ensuring smooth operation.
·Alloy Cast Iron
Alloy cast iron is often alloyed and heat-treated for high-temperature switchgear parts and heavily worn electrical transmission components to enhance wear and heat resistance.
Steel
Steel can be manufactured into load-bearing, transmission, and protective components through casting or forging, casting, cold rolling, and heat treatment, ensuring the long-term reliability of electrical equipment.
·Carbon steel
Carbon steel is often forged or machined into fasteners, guide rails, brackets, and motor shafts, capable of withstanding the torque and loads encountered during installation and operation.
·Low-alloy steel
Low-alloy steel is often forged or welded into heavy-duty circuit breaker supports and busbar clamps, offering excellent fatigue resistance and suitability for long-term live operation.
·Cast steel
Cast steel is commonly used in sand casting motor end covers, pump bodies, and switchgear housings, with subsequent machining ensuring assembly precision and sealing performance.
·Stainless steel
Stainless steel can be manufactured into outdoor lighting fixture housings, control cabinets, fasteners, and pipe fittings through precision casting or sheet metal stamping, maintaining stability in humid and corrosive environments.
Aluminum Alloy
Aluminum alloys are manufactured through die-casting, extrusion, welding, and machining to produce housings, brackets, and heat sinks, achieving a balance of lightweight, heat dissipation, and corrosion resistance.
· Aluminum-Silicon Alloys
Aluminum-silicon alloys are commonly used in die-casting to manufacture lamp housings, heat sinks, and motor casings, ensuring excellent heat dissipation and dimensional accuracy.
· Aluminum-Magnesium Alloys
Aluminum-magnesium alloys are used in outdoor light poles, light fixtures, and electrical enclosures through extrusion and welding, offering excellent corrosion resistance.
· High-Strength Aluminum Alloys
High-strength aluminum alloys undergo solution and aging heat treatments and are then machined into load-bearing frames and busbar duct enclosures, providing sufficient strength.
· Extruded Profiles
Extruded profiles can be cut and processed into heat sinks, guide rails, and profiled enclosures to meet diverse assembly requirements. They can also be anodized for enhanced wear resistance.
Other Metal Alloys
These metals are often used in applications requiring electrical conductivity, corrosion resistance, wear resistance, or high-temperature resistance. Casting, forging, or machining ensures performance and precision.
·Copper and copper alloys
Copper and copper alloys can be extruded or forged to produce busbars, terminals, contacts, and slip rings, ensuring excellent electrical conductivity.
Bronze can be cast or machined into bushings, worm gears, plain bearings, and guides, offering wear resistance and anti-seizure properties, ensuring smooth operation.
Brass is easy to cut and suitable for manufacturing seals and fasteners such as pipe fittings, valve bodies, and nuts. It is corrosion-resistant and easy to assemble.
·Magnesium alloys
Magnesium alloys are die-cast to create lightweight housings and heat sinks, reducing the weight of portable appliances.
·Nickel and nickel alloys
Nickel and nickel alloys are often rolled or precision-cast for heating elements, terminals, and high-temperature, corrosion-resistant components, ensuring long-term, stable operation.
Cast Iron
In the electrical equipment and lighting industries, cast iron is used to manufacture housings and supporting components with high rigidity and excellent vibration absorption. Sand casting, lost foam casting, and subsequent machining are often used to achieve complex shapes and stable dimensions.
·Gray Cast Iron
Gray cast iron is often sand-casted to form motor bases, transformer housings, and equipment support frames. It offers excellent vibration absorption, reducing operating noise and mechanical vibration.
·Ductile Iron
Ductile iron, achieved through sand casting and heat treatment, achieves high strength and toughness. It is suitable for switchgear brackets, distribution box bases, and high-strength mounting brackets, ensuring stability under operating conditions such as opening and closing and vibration.
·Compacted Graphite Iron
Compacted graphite iron offers a balance of strength and vibration absorption, making it suitable for large motor housings and generator bases. Temperature-controlled casting ensures uniform microstructure, ensuring smooth operation.
·Alloy Cast Iron
Alloy cast iron is often alloyed and heat-treated for high-temperature switchgear parts and heavily worn electrical transmission components to enhance wear and heat resistance.
Steel
Steel can be manufactured into load-bearing, transmission, and protective components through casting or forging, casting, cold rolling, and heat treatment, ensuring the long-term reliability of electrical equipment.
·Carbon steel
Carbon steel is often forged or machined into fasteners, guide rails, brackets, and motor shafts, capable of withstanding the torque and loads encountered during installation and operation.
·Low-alloy steel
Low-alloy steel is often forged or welded into heavy-duty circuit breaker supports and busbar clamps, offering excellent fatigue resistance and suitability for long-term live operation.
·Cast steel
Cast steel is commonly used in sand casting motor end covers, pump bodies, and switchgear housings, with subsequent machining ensuring assembly precision and sealing performance.
·Stainless steel
Stainless steel can be manufactured into outdoor lighting fixture housings, control cabinets, fasteners, and pipe fittings through precision casting or sheet metal stamping, maintaining stability in humid and corrosive environments.
Aluminum Alloy
Aluminum alloys are manufactured through die-casting, extrusion, welding, and machining to produce housings, brackets, and heat sinks, achieving a balance of lightweight, heat dissipation, and corrosion resistance.
· Aluminum-Silicon Alloys
Aluminum-silicon alloys are commonly used in die-casting to manufacture lamp housings, heat sinks, and motor casings, ensuring excellent heat dissipation and dimensional accuracy.
· Aluminum-Magnesium Alloys
Aluminum-magnesium alloys are used in outdoor light poles, light fixtures, and electrical enclosures through extrusion and welding, offering excellent corrosion resistance.
· High-Strength Aluminum Alloys
High-strength aluminum alloys undergo solution and aging heat treatments and are then machined into load-bearing frames and busbar duct enclosures, providing sufficient strength.
· Extruded Profiles
Extruded profiles can be cut and processed into heat sinks, guide rails, and profiled enclosures to meet diverse assembly requirements. They can also be anodized for enhanced wear resistance.
Other Metal Alloys
These metals are often used in applications requiring electrical conductivity, corrosion resistance, wear resistance, or high-temperature resistance. Casting, forging, or machining ensures performance and precision.
·Copper and copper alloys
Copper and copper alloys can be extruded or forged to produce busbars, terminals, contacts, and slip rings, ensuring excellent electrical conductivity.
Bronze can be cast or machined into bushings, worm gears, plain bearings, and guides, offering wear resistance and anti-seizure properties, ensuring smooth operation.
Brass is easy to cut and suitable for manufacturing seals and fasteners such as pipe fittings, valve bodies, and nuts. It is corrosion-resistant and easy to assemble.
·Magnesium alloys
Magnesium alloys are die-cast to create lightweight housings and heat sinks, reducing the weight of portable appliances.
·Nickel and nickel alloys
Nickel and nickel alloys are often rolled or precision-cast for heating elements, terminals, and high-temperature, corrosion-resistant components, ensuring long-term, stable operation.
How To Customize Electrical & Lighting Parts
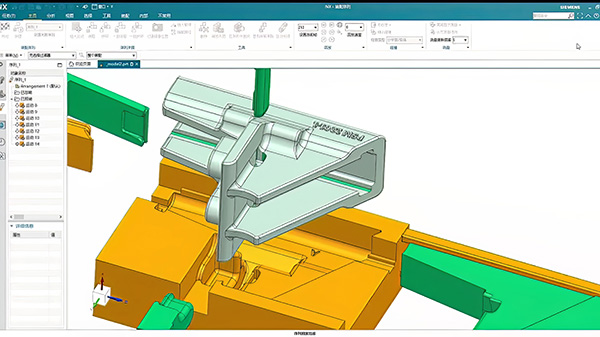
3D Drawings
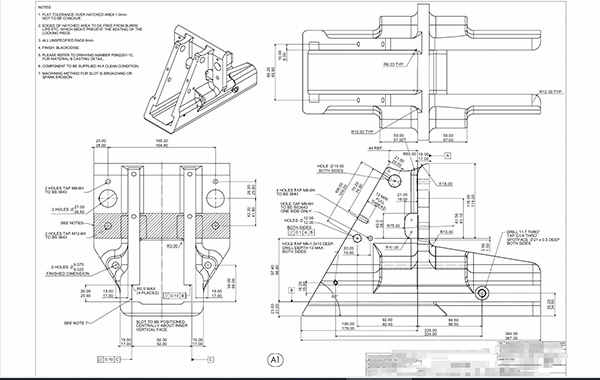
Processing Drawings

Sample
1. Provide Detailed Design Documents Or Samples
2. Confirm Material/Process/Performance
3. Make Molds And Samples
4. Comprehensive Sample Inspection
5. Mass Production
6. Post-production product quality inspection
1. Provide Detailed Design Documents Or Samples
2. Confirm Material/Process/Performance
3. Make Molds And Samples
4. Comprehensive Sample Inspection
5. Mass Production
6. Post-production product quality inspection
Custom Processing Of Electrical & Lighting Parts

Casting
In the electrical equipment and lighting industry, casting processes are used to manufacture components such as lampshades, electrical housings and transformers, which can withstand high electrical loads and dissipate heat, thus ensuring the service life and safety of electrical equipment and lighting systems.

Forging
In electrical equipment and lighting, forging processes are used to produce components such as connectors, switchgear components and structural frames to improve mechanical strength, conductivity and durability under high loads or frequent use.

Heat Treatment
In the electrical equipment and lighting industries, heat treatment processes are used to improve the performance and durability of electrical contacts, switch assemblies and power connectors. They help optimize the material's resistance to wear, corrosion and arcing, thereby extending the service life of critical components under frequent operation and environmental stress.

Machining
In electrical equipment and lighting, machining can manufacture precision components such as electrical connectors, terminals and heat sinks. The precision provided by machining ensures that these parts meet strict electrical and mechanical tolerances, ensuring the efficient and safe operation of lighting systems, circuit boards and other electrical equipment.

Sheet Metal Fabrication
In the electrical equipment and lighting sector, sheet metal fabrication is used to produce lightweight, durable components such as electrical enclosures, light brackets and heat shields to protect electrical systems from external elements, improve thermal management and provide structural support for lighting equipment and power distribution equipment.

Surface Treatment
In electrical equipment and lighting, surface treatment processes are used to improve corrosion resistance, reduce electrical resistance, and enhance aesthetics. For example, the aluminum housings of lighting fixtures and electrical enclosures are often anodized to prevent corrosion, while electrical contacts may be silver or gold plated to ensure reliable conductivity and reduce wear over time.














