Manufacturing Process of Cast Iron Parts

Iron Sand Casting
Iron sand casting uses sand as the casting material, then pours molten iron into the mold, removes the iron casting after cooling, cleans and post-processes.
· The mold manufacturing cost is low and can be used many times
· Casts large and medium-sized cast iron castings with complex shapes and large sizes.
· Suitable for small, medium and large batch production.

Iron Shell Mold Casting
Iron shell mold casting uses ceramic or other refractory materials as the casting mold, and the casting mold is usually made by applying multiple layers of refractory coating on the surface of the model.
· Suitable for small batches or high-value iron castings
· Used to produce small and medium-sized iron castings
· Make complex iron castings

Iron Lost Foam Casting
Iron lost foam casting is to form a casting mold by coating a layer of sand on a combustible model (such as foam plastic). This process does not require the removal of the foam model.
· Directly produce iron castings with complex shapes
· Lower cost and higher production efficiency
· Suitable for the production of small and medium-sized iron castings

Heat Treatment
Heat treatment is to change the internal structure and properties of iron materials through heating, insulation, cooling and other processes, improve the mechanical properties of metals, extend service life, and optimize processing performance.
· Improve the hardness and strength of cast iron parts
· Improve the toughness of cast iron parts
· Improve the wear resistance and corrosion resistance of cast iron parts

Machining
Machining is a post-processing process for cast iron parts, which improves the accuracy, surface quality and functionality of iron castings through fine machining.
· Optimize appearance quality
· Improve cast iron part structure and function
· Process thin walls and complex shapes

Surface Treatment
Surface treatment can change the surface of iron castings by physical, chemical or mechanical means to improve the surface quality of iron castings, increase their durability, and improve appearance and functionality.
· Improve surface hardness
· Improve appearance and improve dimensional accuracy
· Improve adhesion and corrosion resistance
Different Materials of Iron Castings
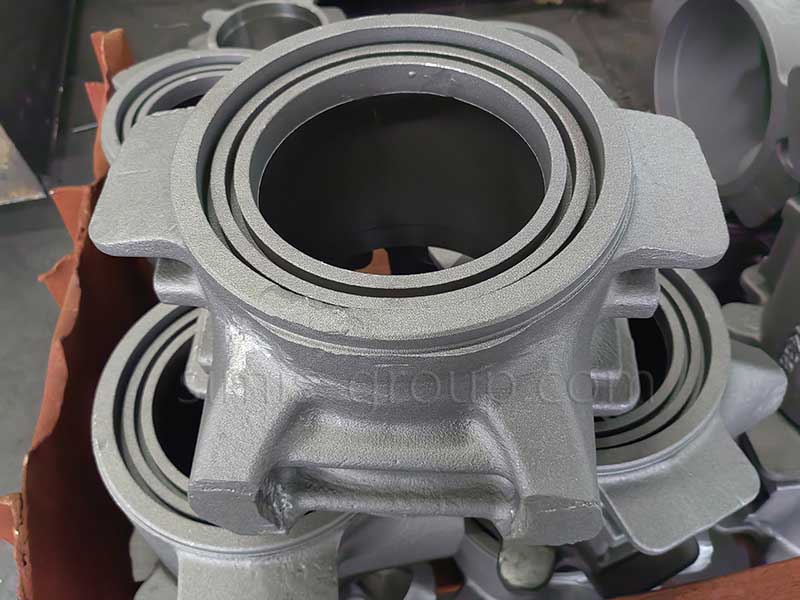
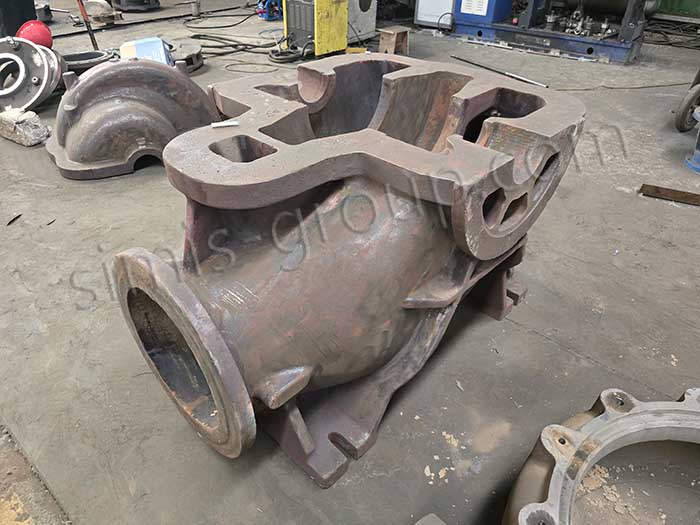



Gray (grey) iron
Gray (grey) iron has moderate strength, good castability, thermal conductivity, shock absorption and wear resistance, low cost, and is suitable for the production of castings with complex shapes and large sizes.
· Good castability: easy to cast, suitable for the production of castings with complex shapes and large sizes.
· Good shock absorption performance: the presence of graphite gives gray iron good shock absorption performance.
· Good wear resistance: suitable for manufacturing friction parts such as engine cylinders and brake discs.
· Good thermal conductivity: suitable for parts with high heat dissipation requirements.
· Good processing performance: moderate hardness, less wear on processing tools, suitable for mechanical processing.
Grey iron parts by Simis Iron Foundry:
Brake discs, engine cylinders, machine tool beds, pump housings, valve bodies, piping systems, etc.
Gray iron casting grades used by Simis Iron Foundry:
ISO 185 / EN 1561: EN-GJL-100, EN-GJL-150, EN-GJL-200, EN-GJL-250, EN-GJL-300, EN-GJL-350.
ASTM A48: Class 20, Class 25, Class 30, Class 35, Class 40, Class 45, Class 50, Class 55, Class 60.
DIN: GG-10, GG-15, GG-20, GG-25, GG-30, GG-35.
JIS G5501: FC100, FC150, FC200, FC250, FC300, FC350.
Ductile Iron
Ductile iron uses a nodularizing agent (usually magnesium or cerium) to create spherical graphite, rather than the flakes found in gray iron. This spherical graphite form fundamentally eliminates the stress concentration effects of flake graphite, allowing it to combine the excellent properties of cast iron with the high strength and toughness of steel. Ductile iron offers high strength, good toughness, excellent castability, wear resistance, vibration resistance, and machinability. Its overall performance is similar to that of steel, but at a lower cost, making it an ideal material for manufacturing high-performance, high-reliability, complex structural parts.
· High Strength and Toughness: The spherical graphite minimizes the chance of fracture in the matrix, giving ductile iron significantly greater strength and impressive toughness than gray iron, with an elongation of over 20%.
· Excellent Castability: Its excellent fluidity and lower shrinkage than cast steel make it easy to cast complex, thin-walled, and thick, large-section castings.
· Excellent Wear Resistance: Its dense matrix structure and the graphite nodules itself act as excellent lubricants, making it ideal for manufacturing parts subject to friction.
· Good Machinability: Despite its high strength, it still offers good machinability.
· Good Vibration Resistance and Thermal Conductivity: It inherits the vibration resistance and thermal conductivity advantages of cast iron, yet outperforms cast steel.
Casting ductile iron parts by Simis Iron Foundry:
Automotive parts (crankshafts, steering knuckles, differential housings), gears, large agricultural machinery components, valves and piping systems (such as water mains), rollers, pressure vessel housings, etc.
Ductile iron casting grades used by Simis Iron Foundry :
ISO 1083 / EN 1563: EN-GJS-350-22, EN-GJS-400-18, EN-GJS-500-7, EN-GJS-600-3, EN-GJS-700-2, EN-GJS-800-2
ASTM A536: 60-40-18, 65-45-12, 80-55-06, 100-70-03, 120-90-02
DIN: GGG-40, GGG-50, GGG-60, GGG-70, GGG-80
JIS G5502: FCD400, FCD450, FCD500, FCD600, FCD700
Austempered Ductile Iron / ADI
Austempered ductile iron (ADI) is an advanced engineering material with high strength, high toughness, and high wear resistance, achieved through the "austenitic austempering" heat treatment of high-quality ductile iron. Unlike ordinary ductile iron, ADI utilizes a unique heat treatment process to achieve a matrix dominated by "ausferrite," rather than altering its chemical composition. The overall performance of ADI far exceeds that of ordinary ductile iron and even surpasses many forged and cast steels, achieving a perfect combination of lightweight, high performance, and low cost.
· Extremely High Strength and Toughness Combination: The unique austenitic microstructure enables ultra-high strength (up to 1600 MPa) combined with excellent toughness and elongation, resulting in a superior strength-to-weight ratio compared to aluminum alloys and cast steel.
· Excellent Wear Resistance: Its high surface hardness and strong work-hardening capability provide exceptional wear resistance under friction and impact loads, two to three times that of hardened steel. · Excellent Fatigue Resistance: The combination of high strength and toughness provides high resistance to bending and contact fatigue, making it suitable for parts subjected to cyclic loads.
· Good Vibration Damping Performance: Retaining its graphite nodule structure, it offers 3-5 times the vibration damping performance of steel, helping to reduce noise and vibration.
· Good Machinability and Lightweighting Potential: It can be machined before heat treatment. Its high strength allows for thinner and lighter designs, making it an ideal material for lightweighting parts.
Austempered ductile iron parts by Simis Iron Foundry:
Gears, suspension components, and engine crankshafts for heavy-duty trucks and rail transit; track shoes, sprockets, and drive gears for construction machinery; cutting tools and gears for agricultural machinery; high-performance reducer gears and camshafts; and mining machinery components requiring high safety.
Austempered ductile iron parts grades used by Simis Iron Foundry:
ASTM A897M: Grade 1: 1250/850/10, Grade 2: 1500/1100/7, Grade 3: 1750/1300/4, Grade 4: 2000/1550/1, Grade 5: 2300/1850/ --
ISO 17804/EN 1564: EN-GJS-800-8, EN-GJS-900-8, EN-GJS-1050-6, EN-GJS-1200-3, EN-GJS-1400-1, EN-GJS-1600-1
Alloy Cast Iron
Alloy cast iron is a cast iron material made by intentionally adding one or more alloying elements (such as chromium, nickel, molybdenum, copper, silicon, and manganese) to ordinary gray cast iron or ductile iron to significantly improve specific properties (such as wear resistance, heat resistance, and corrosion resistance). The selection of alloy cast iron material depends on the specific application conditions (such as wear type, operating temperature, and corrosive media). Through alloying, the appropriate alloy composition and grade are selected. This alloying process achieves comprehensive or specialized properties superior to those of ordinary cast iron, meeting the demands of demanding applications.
· Excellent Wear Resistance: The addition of elements such as chromium, molybdenum, and vanadium forms high-hardness carbides, significantly improving resistance to abrasive wear and tear. It is suitable for use in heavy-wear environments such as mining and cement production.
· Good Heat Resistance: The addition of elements such as silicon, aluminum, and chromium forms a dense oxide film (such as SiO₂ and Al₂O₃) on the surface, preventing further oxidation and improving resistance to high-temperature growth and oxidation. It is suitable for furnace components.
· Excellent Corrosion Resistance: The addition of elements such as silicon, chromium, and nickel increases the matrix's electrode potential and passivation ability, significantly enhancing its resistance to corrosion from media such as acids, alkalis, and salt water.
· Higher Strength and Hardness: Alloying elements produce solid solution strengthening and refine the microstructure, thereby improving the strength, hardness, and hardenability of cast iron.
· Excellent Overall Performance: Through a multi-alloy formulation, multiple properties such as wear resistance, heat resistance, and corrosion resistance can be simultaneously achieved.
Casting alloy cast iron parts by Simis Iron Foundry:
Wear-Resistant Parts: Rollers, Shot Blasting Machine Blades, Liners, Slurry Pump Casings.
Heat-Resistant Parts: Boiler Grate, Heat Exchangers, Heat Treatment Furnace Floors, Flue Gates.
Corrosion-Resistant Parts: Chemical Valves, Pump Casings, Pipes, Pickling Tanks.
Special-Purpose Parts: Machine Tool Guides, Cylinder Liners, Automotive Camshafts.
Casting alloy cast iron grades used by Simis Iron Foundry :
-- Wear-Resistant Alloy Cast Iron
High Chromium Cast Iron: ASTM A532 Class III Type A, KmTBCr26, LCN250
Nickel-Chromium Cast Iron (Ni-Hard): ASTM A532 Class I Type A, Ni-Hard 4
-- Heat-Resistant Alloy Cast Iron
Medium Silicon Heat-Resistant Cast Iron: RTSi-5.5 (Silicon Content Approximately 5.5%)
High Aluminum Heat-Resistant Cast Iron: RQTAI22 (Aluminum Content Approximately 22%)
Chromium Heat-Resistant Cast Iron: RTCr16 (Chromium Content Approximately 16%)
-- Corrosion-Resistant Alloy Cast Iron
High Silicon Cast Iron (Silicon Austenitic Cast Iron): ISO 2892 Grade F15 (Si Content Approximately 15%), ASTM A518 Grade 3 (Si Content Approximately 14.5%) - Known for its exceptionally high acid resistance.
Gray (grey) iron
Gray (grey) iron has moderate strength, good castability, thermal conductivity, shock absorption and wear resistance, low cost, and is suitable for the production of castings with complex shapes and large sizes.
· Good castability: easy to cast, suitable for the production of castings with complex shapes and large sizes.
· Good shock absorption performance: the presence of graphite gives gray iron good shock absorption performance.
· Good wear resistance: suitable for manufacturing friction parts such as engine cylinders and brake discs.
· Good thermal conductivity: suitable for parts with high heat dissipation requirements.
· Good processing performance: moderate hardness, less wear on processing tools, suitable for mechanical processing.
Grey iron parts by Simis Iron Foundry:
Brake discs, engine cylinders, machine tool beds, pump housings, valve bodies, piping systems, etc.
Gray iron casting grades used by Simis Iron Foundry:
ISO 185 / EN 1561: EN-GJL-100, EN-GJL-150, EN-GJL-200, EN-GJL-250, EN-GJL-300, EN-GJL-350.
ASTM A48: Class 20, Class 25, Class 30, Class 35, Class 40, Class 45, Class 50, Class 55, Class 60.
DIN: GG-10, GG-15, GG-20, GG-25, GG-30, GG-35.
JIS G5501: FC100, FC150, FC200, FC250, FC300, FC350.
Ductile Iron
Ductile iron uses a nodularizing agent (usually magnesium or cerium) to create spherical graphite, rather than the flakes found in gray iron. This spherical graphite form fundamentally eliminates the stress concentration effects of flake graphite, allowing it to combine the excellent properties of cast iron with the high strength and toughness of steel. Ductile iron offers high strength, good toughness, excellent castability, wear resistance, vibration resistance, and machinability. Its overall performance is similar to that of steel, but at a lower cost, making it an ideal material for manufacturing high-performance, high-reliability, complex structural parts.
· High Strength and Toughness: The spherical graphite minimizes the chance of fracture in the matrix, giving ductile iron significantly greater strength and impressive toughness than gray iron, with an elongation of over 20%.
· Excellent Castability: Its excellent fluidity and lower shrinkage than cast steel make it easy to cast complex, thin-walled, and thick, large-section castings.
· Excellent Wear Resistance: Its dense matrix structure and the graphite nodules itself act as excellent lubricants, making it ideal for manufacturing parts subject to friction.
· Good Machinability: Despite its high strength, it still offers good machinability.
· Good Vibration Resistance and Thermal Conductivity: It inherits the vibration resistance and thermal conductivity advantages of cast iron, yet outperforms cast steel.
Casting ductile iron parts by Simis Iron Foundry:
Automotive parts (crankshafts, steering knuckles, differential housings), gears, large agricultural machinery components, valves and piping systems (such as water mains), rollers, pressure vessel housings, etc.
Ductile iron casting grades used by Simis Iron Foundry :
ISO 1083 / EN 1563: EN-GJS-350-22, EN-GJS-400-18, EN-GJS-500-7, EN-GJS-600-3, EN-GJS-700-2, EN-GJS-800-2
ASTM A536: 60-40-18, 65-45-12, 80-55-06, 100-70-03, 120-90-02
DIN: GGG-40, GGG-50, GGG-60, GGG-70, GGG-80
JIS G5502: FCD400, FCD450, FCD500, FCD600, FCD700
Austempered Ductile Iron / ADI
Austempered ductile iron (ADI) is an advanced engineering material with high strength, high toughness, and high wear resistance, achieved through the "austenitic austempering" heat treatment of high-quality ductile iron. Unlike ordinary ductile iron, ADI utilizes a unique heat treatment process to achieve a matrix dominated by "ausferrite," rather than altering its chemical composition. The overall performance of ADI far exceeds that of ordinary ductile iron and even surpasses many forged and cast steels, achieving a perfect combination of lightweight, high performance, and low cost.
· Extremely High Strength and Toughness Combination: The unique austenitic microstructure enables ultra-high strength (up to 1600 MPa) combined with excellent toughness and elongation, resulting in a superior strength-to-weight ratio compared to aluminum alloys and cast steel.
· Excellent Wear Resistance: Its high surface hardness and strong work-hardening capability provide exceptional wear resistance under friction and impact loads, two to three times that of hardened steel. · Excellent Fatigue Resistance: The combination of high strength and toughness provides high resistance to bending and contact fatigue, making it suitable for parts subjected to cyclic loads.
· Good Vibration Damping Performance: Retaining its graphite nodule structure, it offers 3-5 times the vibration damping performance of steel, helping to reduce noise and vibration.
· Good Machinability and Lightweighting Potential: It can be machined before heat treatment. Its high strength allows for thinner and lighter designs, making it an ideal material for lightweighting parts.
Austempered ductile iron parts by Simis Iron Foundry:
Gears, suspension components, and engine crankshafts for heavy-duty trucks and rail transit; track shoes, sprockets, and drive gears for construction machinery; cutting tools and gears for agricultural machinery; high-performance reducer gears and camshafts; and mining machinery components requiring high safety.
Austempered ductile iron parts grades used by Simis Iron Foundry:
ASTM A897M: Grade 1: 1250/850/10, Grade 2: 1500/1100/7, Grade 3: 1750/1300/4, Grade 4: 2000/1550/1, Grade 5: 2300/1850/ --
ISO 17804/EN 1564: EN-GJS-800-8, EN-GJS-900-8, EN-GJS-1050-6, EN-GJS-1200-3, EN-GJS-1400-1, EN-GJS-1600-1
Alloy Cast Iron
Alloy cast iron is a cast iron material made by intentionally adding one or more alloying elements (such as chromium, nickel, molybdenum, copper, silicon, and manganese) to ordinary gray cast iron or ductile iron to significantly improve specific properties (such as wear resistance, heat resistance, and corrosion resistance). The selection of alloy cast iron material depends on the specific application conditions (such as wear type, operating temperature, and corrosive media). Through alloying, the appropriate alloy composition and grade are selected. This alloying process achieves comprehensive or specialized properties superior to those of ordinary cast iron, meeting the demands of demanding applications.
· Excellent Wear Resistance: The addition of elements such as chromium, molybdenum, and vanadium forms high-hardness carbides, significantly improving resistance to abrasive wear and tear. It is suitable for use in heavy-wear environments such as mining and cement production.
· Good Heat Resistance: The addition of elements such as silicon, aluminum, and chromium forms a dense oxide film (such as SiO₂ and Al₂O₃) on the surface, preventing further oxidation and improving resistance to high-temperature growth and oxidation. It is suitable for furnace components.
· Excellent Corrosion Resistance: The addition of elements such as silicon, chromium, and nickel increases the matrix's electrode potential and passivation ability, significantly enhancing its resistance to corrosion from media such as acids, alkalis, and salt water.
· Higher Strength and Hardness: Alloying elements produce solid solution strengthening and refine the microstructure, thereby improving the strength, hardness, and hardenability of cast iron.
· Excellent Overall Performance: Through a multi-alloy formulation, multiple properties such as wear resistance, heat resistance, and corrosion resistance can be simultaneously achieved.
Casting alloy cast iron parts by Simis Iron Foundry:
Wear-Resistant Parts: Rollers, Shot Blasting Machine Blades, Liners, Slurry Pump Casings.
Heat-Resistant Parts: Boiler Grate, Heat Exchangers, Heat Treatment Furnace Floors, Flue Gates.
Corrosion-Resistant Parts: Chemical Valves, Pump Casings, Pipes, Pickling Tanks.
Special-Purpose Parts: Machine Tool Guides, Cylinder Liners, Automotive Camshafts.
Casting alloy cast iron grades used by Simis Iron Foundry :
-- Wear-Resistant Alloy Cast Iron
High Chromium Cast Iron: ASTM A532 Class III Type A, KmTBCr26, LCN250
Nickel-Chromium Cast Iron (Ni-Hard): ASTM A532 Class I Type A, Ni-Hard 4
-- Heat-Resistant Alloy Cast Iron
Medium Silicon Heat-Resistant Cast Iron: RTSi-5.5 (Silicon Content Approximately 5.5%)
High Aluminum Heat-Resistant Cast Iron: RQTAI22 (Aluminum Content Approximately 22%)
Chromium Heat-Resistant Cast Iron: RTCr16 (Chromium Content Approximately 16%)
-- Corrosion-Resistant Alloy Cast Iron
High Silicon Cast Iron (Silicon Austenitic Cast Iron): ISO 2892 Grade F15 (Si Content Approximately 15%), ASTM A518 Grade 3 (Si Content Approximately 14.5%) - Known for its exceptionally high acid resistance.
Application of Iron Castings
Custom Iron Castings by Simis Iron Foundry
Iron Castings Company's Custom Steps
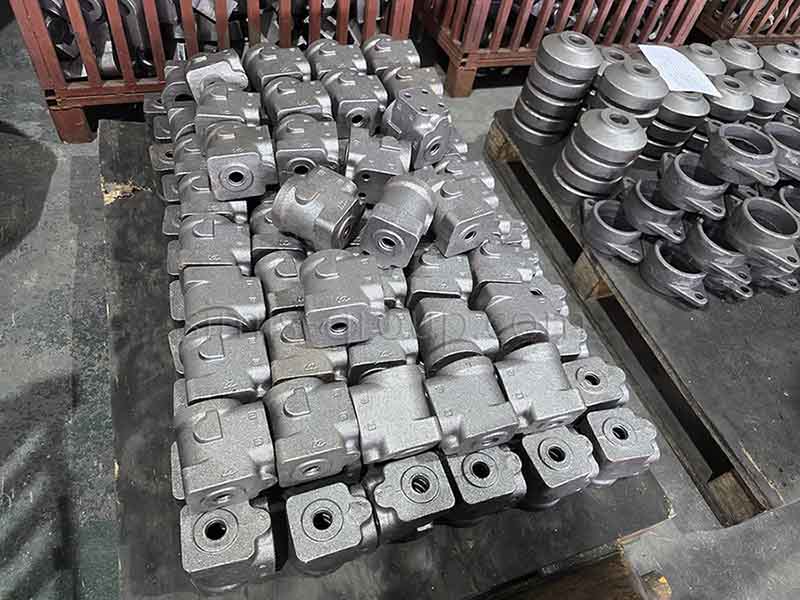

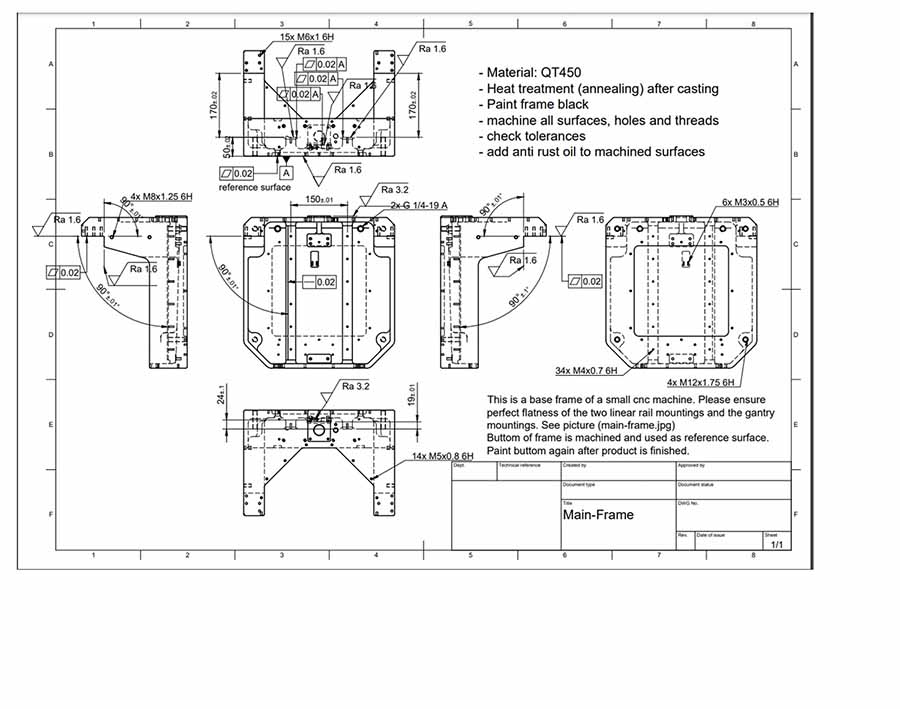

Confirm the customization requirements of cast iron parts
1. Provide detailed design documents or samples of cast iron parts
Simis engineers will analyze the 3D drawings (CAD models) and corresponding plane drawings of the parts provided by the customer to ensure that the design drawings meet the manufacturing requirements.
Whether to provide samples: If the customer can provide samples, we will produce according to the samples.
2. Confirm the requirements of various product attributes
Understand the various performance requirements of the parts, such as strength, hardness, wear resistance, corrosion resistance, etc., as well as the size, tolerance, and accuracy of the parts, and confirm the requirements of surface roughness, appearance quality, etc.
3. Confirm the material of the casting
According to the use environment, technical requirements or customer requirements of the parts, select the appropriate cast iron material. Our engineers will give suggestions based on the price, mechanical properties, wear resistance, corrosion resistance, etc. of the material.
4. Confirm the casting process of the parts
According to customer needs, combined with the requirements of part price, shape, dimensional accuracy, material, etc., determine the casting process suitable for part production.
5. Make molds and samples
According to the drawings or samples provided by the customer, make casting molds that meet the requirements, and cast the selected cast iron material through the corresponding process to produce the first batch of samples.
6. Comprehensive inspection of samples
The samples produced will be fully inspected to ensure that they meet the design standards and customer quality requirements,
and test reports such as size and tolerance inspection, performance testing, chemical composition analysis, and non-destructive testing.
Production and quality control
7. Mass production
After the sample is confirmed and approved by the customer, the mass production plan is arranged according to the order requirements and the production materials are prepared.
The same casting equipment and process as the sample stage are used in the mass production process to ensure the consistency of each batch of cast iron castings.
8. Quality control in mass production
We implement strict quality control measures during the production process: regular sampling during the production process to check the size, appearance, physical properties, etc. of cast iron parts to ensure the consistency of each batch of parts and meet customer requirements.
9. Product quality inspection after production
Multiple inspections by multiple people: We will arrange different inspectors to conduct multiple sampling inspections on the final product, including dimensional accuracy, surface quality, strength, hardness, etc., to ensure that the produced cast iron parts meet customer requirements.
10. Parts packaging and delivery
Packaging: Pack and ship the parts that have passed the quality inspection, choose the appropriate packaging method and the appropriate logistics method (such as air, sea, and land transportation) to avoid damage during transportation and deliver them to customers on time.




If you want to custom parts, please send me the design drawings and 3D drawings of theparts you want to customize by email, and we will calculate an accurate price for you bylooking at the detailed part parameters and 3D model.




















































