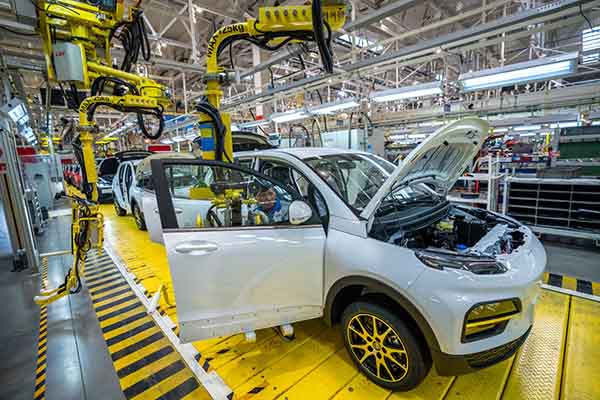
Manufacturing Process of Aluminum Forging Parts

Aluminum Closed Die Forging
Aluminum closed die forging is to heat the aluminum material to a certain temperature and then forge it through a special closed die. It can produce aluminum forgings with high precision, excellent mechanical properties and good surface quality.
· Suitable for mass production
· High dimensional accuracy of aluminum forgings
· Excellent mechanical properties of aluminum forgings

Aluminum Ring Forging
Aluminum ring forging is specially used to produce ring parts. After heating the aluminum blank, it is placed in a mold or forging equipment, and pressure is applied to force the metal to flow into the mold cavity to form a ring forging.
· Used to make parts with complex shapes
· Suitable for medium and large-scale production
· Aluminum forgings have high strength and toughness
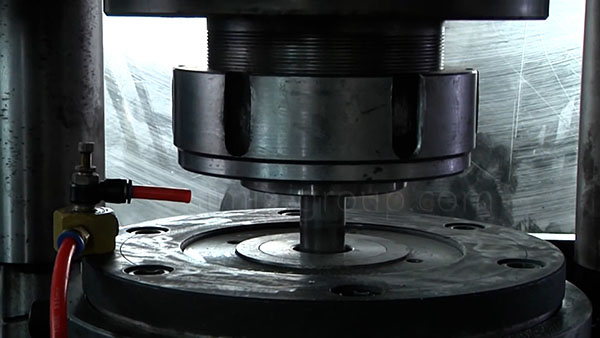
Aluminum Cold Forging
Aluminum cold forging is the process of plastically deforming a aluminum blank by applying pressure at room temperature without heating, thereby achieving high precision and improved mechanical properties.
· Tight tolerances and good surface finish
· Increased strength and hardness of the aluminum, improving durability
· Reduced material waste and the need for secondary processing
· Aluminum Forgings have higher strength and toughness
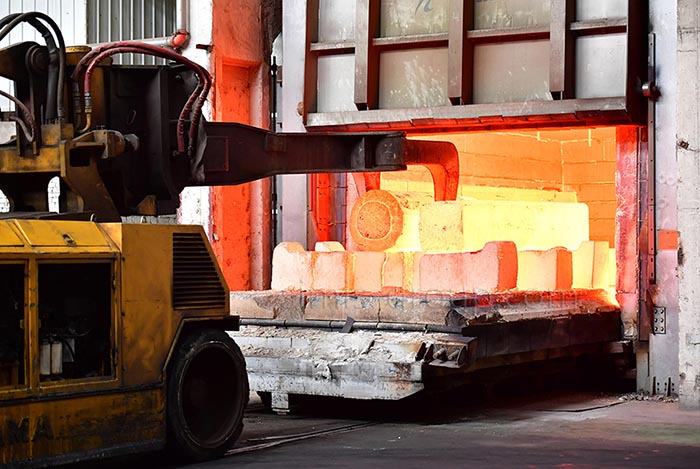

Heat Treatment
Heat treatment is to change the internal structure and properties of metal materials by heating, heat preservation and cooling, improve the mechanical properties of aluminum, extend service life and optimize processing performance.
· Improve the hardness and strength of aluminum materials
· Improve the toughness of aluminum materials
· Improve wear resistance and corrosion resistance
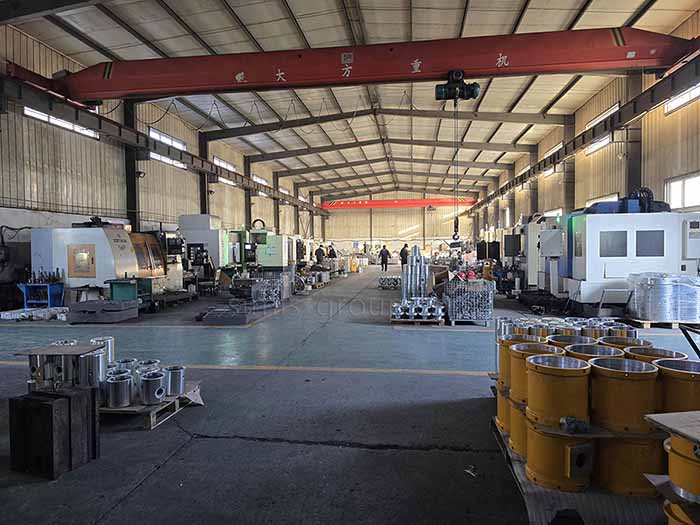

Machining
Machining is a post-processing process for aluminum forings, which improves the accuracy, surface quality and functionality of forgings through fine processing.
· Optimize appearance quality
· Improve part structure and function
· Process thin walls and complex shapes

Surface Treatment
Surface treatment can change the surface of forgings by physical, chemical or mechanical methods to improve the surface quality of aluminum forgings, increase their durability, and improve appearance and functionality.
· Improve surface hardness
· Improve appearance and improve dimensional accuracy
· Improve adhesion and corrosion resistance
Different Materials of Aluminum Forgings
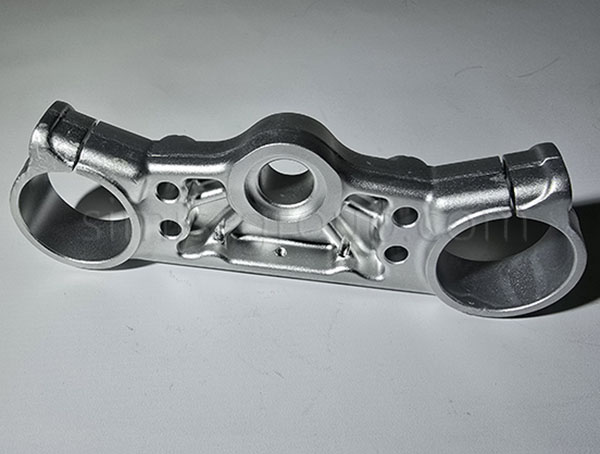
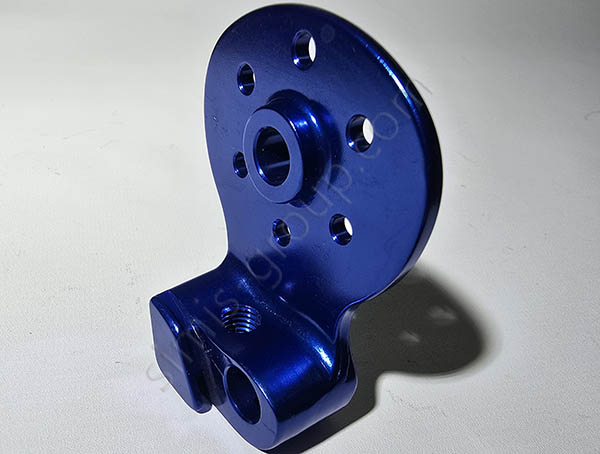
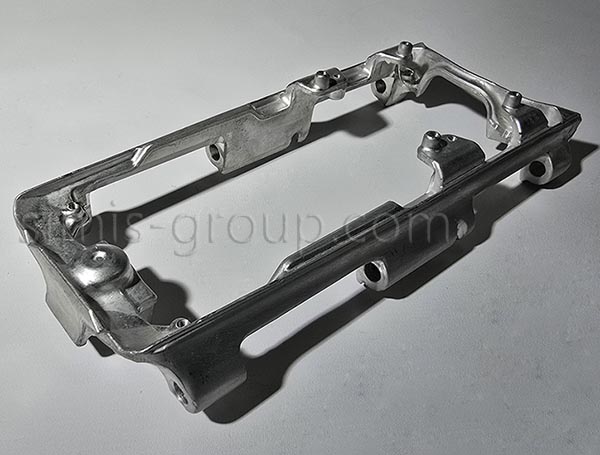



1. Non-Heat-Treatable Aluminum Alloys
Non-heat-treatable aluminum alloys achieve strength through work hardening (or strain hardening) during cold deformation processes (such as cold forging and rolling), rather than through heat treatment to enhance their mechanical properties. The strength of these alloys stems from solid solution strengthening and strain hardening, making them ideal for applications requiring good formability, corrosion resistance, and moderate strength.
· Excellent Corrosion Resistance: Particularly resistant to atmospheric, chemical, and marine corrosion, often outperforming heat-treatable alloys in corrosive environments.
· Good Formability and Workability: Maintain excellent ductility and can be extensively cold worked to achieve higher strength levels through strain hardening.
· Superior Weldability and Joining Characteristics: Generally exhibit better welding performance than heat-treatable alloys, with minimal loss of properties in heat-affected zones.
· Good Electrical and Thermal Conductivity: Maintain high conductivity properties, making them suitable for electrical and thermal management applications.
· Stable Properties at Cryogenic Temperatures: Mechanical properties often improve at low temperatures while maintaining good toughness.
Forged Non-Heat-Treatable Aluminum Components by Simis Aluminum Forging Factory:
Marine and shipbuilding components; chemical processing equipment; electrical busbars and connectors; cryogenic storage tanks; automotive body panels; architectural structures; food processing equipment.
Forged Non-Heat-Treatable Aluminum Alloy Categories used by Simis Aluminum Forging Factory:
· Pure Aluminum and Low-Alloy Forgings
Common Applications: Electrical conductors, heat exchangers, chemical equipment, and decorative applications.
Common Grades: AA 1050 (Al99.5), AA 1060 (Al99.6), AA 1100 (Al99.0Cu)
· Aluminum-Manganese (Al-Mn) Alloy Forgings
Common Applications: Cooking utensils, heat exchangers, storage tanks, and architectural applications.
Common Grades: AA 3003 (AlMn1Cu), AA 3004 (AlMn1Mg1)
· Aluminum-Magnesium (Al-Mg) Alloy Forgings
Common Applications: Marine hardware, boat hull components, pressure vessels, and transportation equipment.
Common Grades: AA 5052 (AlMg2.5), AA 5083 (AlMg4.5Mn0.7), AA 5754 (AlMg3)
· Aluminum-Magnesium-Silicon (Al-Mg-Si) Alloy Forgings
Common Applications: Architectural extrusions, automotive body panels, and general engineering applications.
Common Grades: AA 6061 (AlMg1SiCu), though primarily heat-treatable, some non-heat-treatable variants exist
2. Aluminum-Copper Alloys
Forged aluminum-copper alloys are produced by heating and compression-deforming aluminum-copper alloy billets, followed by solution heat treatment and aging to achieve their optimal mechanical properties. Aluminum-copper alloys are among the strongest aluminum materials, offering an excellent strength-to-weight ratio and good fatigue resistance, making them ideal for high-performance structural applications. However, their corrosion resistance is generally lower than that of other aluminum alloys, and they often require protective coatings or cladding to withstand harsh environments.
· High Strength-to-Weight Ratio: Offer the highest strength levels among aluminum alloys when properly heat-treated, combined with low density.
· Excellent Fatigue Resistance: Good resistance to cyclic loading and vibration, making them suitable for aerospace and automotive applications.
· Good Machinability: Can be machined to precision tolerances and excellent surface finishes in the heat-treated condition.
· Maintain Strength at Elevated Temperatures: Retain mechanical properties better than most other aluminum alloys at temperatures up to 150°C.
· Good Anodizing Response: Can be anodized for improved surface hardness and corrosion resistance.
Forged Aluminum-Copper Components by Simis Aluminum Forging Factory:
Aircraft structural components and fuselage frames; automotive suspension parts and wheels; high-performance sporting goods; robotic arms and machinery parts.
Forged Aluminum-Copper Alloy Categories used by Simis Aluminum Forging Factory:
· Binary Aluminum-Copper Alloy Forgings
Common Applications: General high-strength structural components, automotive parts, and machinery components.
Common Grades: AA 2014 (AlCu4SiMg), AA 2219 (AlCu6Mn)
· Aluminum-Copper with Magnesium Addition Forgings
Common Applications: Aircraft structural members, truck frames, and high-stress components.
Common Grades: AA 2024 (AlCu4Mg1), AA 2017 (AlCu4MgSi)
· Aluminum-Copper with Lithium Addition Forgings
Common Applications: high-performance automotive parts.
Common Grades: AA 2090 (AlCu2Li3), AA 2099 (AlCu2Li1Mg0.5)
· High-Strength Aluminum-Copper Forgings
Common Applications: high-performance racing components.
Common Grades: AA 2618 (AlCu2Mg1.5Ni1), AA 2218 (AlCu4Mg2Ni1)
3. Aluminum-Magnesium-Silicon Alloys
Forged aluminum-magnesium-silicon alloys are manufactured by heating and forming Al-Mg-Si alloy billets through compressive deformation, followed by solution heat treatment and artificial aging to achieve optimal mechanical properties. Aluminum-magnesium-silicon alloys offer an excellent balance of medium-to-high strength, good corrosion resistance, and exceptional extrudability, making them one of the most versatile and widely used aluminum alloy families.
· Good Strength-to-Weight Ratio: Provide medium to high strength levels after heat treatment, combined with low density for weight-sensitive applications.
· Excellent Corrosion Resistance: Demonstrate very good resistance to atmospheric and marine corrosion, superior to most aluminum-copper alloys.
· Good Formability and Weldability: Can be easily formed and welded using various methods while maintaining good mechanical properties.
· Excellent Extrudability: Among the best extrudable aluminum alloys, allowing complex cross-sectional profiles to be produced.
· Good Machinability: Can be machined to precision tolerances and good surface finishes in the heat-treated condition.
Forged Aluminum-Magnesium-Silicon Components by Simis Aluminum Forging Factory:
Automotive chassis components and body structures; bicycle frames and components; architectural extrusions and structures; heat exchanger components; marine fittings and hardware; electrical conductor components; general engineering structural parts.
Forged Aluminum-Magnesium-Silicon Alloy Categories used by Simis Aluminum Forging Factory:
· Balanced Mg₂Si Alloy Forgings
Common Applications: General structural components, automotive parts, and architectural applications.
Common Grades: AA 6061 (AlMg1SiCu), AA 6063 (AlMg0.7Si)
· High-Silicon Alloy Forgings
Common Applications: High-strength structural components, wear-resistant parts, and automotive suspension components.
Common Grades: AA 6082 (AlMg1SiMn), AA 6005 (AlMg0.8Si)
· High-Magnesium Alloy Forgings
Common Applications: Marine structures, pressure vessels, and transportation equipment components.
Common Grades: AA 6101 (AlMg0.6Si), AA 6151 (AlMg1SiCr)
· Copper-Containing Alloy Forgings
Common Applications: High-strength structural components, aerospace parts, and precision machinery components.
Common Grades: AA 6061 (AlMg1SiCu), AA 6013 (AlMg1SiCuMn)
4. Aluminum-Zinc Alloys
Forged aluminum-zinc alloys are produced by heating and compression-deforming aluminum-zinc alloy billets. They utilize their natural aging properties to achieve high strength without the need for solution heat treatment, making them cost-effective for a variety of structural applications. They are particularly well-suited for applications requiring high strength without complex heat treatment processes.
· High As-Cast Strength: Achieve high mechanical properties in the as-cast condition through natural aging, reducing heat treatment requirements.
· Good Machinability: Can be machined to precision tolerances with good chip formation and surface finish characteristics.
· Excellent Casting Characteristics: Demonstrate good fluidity and feeding characteristics during the casting process.
· Natural Aging Properties: Continue to strengthen naturally at room temperature after solidification.
· Good Corrosion Resistance: Provide adequate resistance to general atmospheric corrosion for most applications.
Forged Aluminum-Zinc Components by Simis Aluminum Forging Factory:
Automotive engine brackets and mounts; structural hardware components; machinery parts and fittings; electrical hardware; general engineering components; architectural fittings.
Forged Aluminum-Zinc Alloy Categories used by Simis Aluminum Forging Factory:
· High-Zinc Aluminum Alloy Forgings
Common Applications: Automotive structural components, high-strength machinery parts, and structural fittings.
Common Grades: AA 7075 (AlZn5.5MgCu), AA 7005 (AlZn4.5Mg1.5Mn)
· Zinc-Magnesium Alloy Forgings
Common Applications: General structural components, marine hardware, and transportation equipment parts.
Common Grades: AA 7108 (AlZn5.5Mg1.5), AA 7003 (AlZn6Mg0.8Zr)
· Zinc-Copper Alloy Forgings
Common Applications: High-strength structural components, aerospace parts, and precision machinery components.
Common Grades: AA 7175 (AlZn5.5MgCu1.5), AA 7475 (AlZn5.5MgCu2)
· Low-Zinc Alloy Forgings
Common Applications: Marine components, architectural structures, and general engineering applications.
Common Grades: AA 7010 (AlZn6MgCu), AA 7020 (AlZn4.5Mg1)
1. Non-Heat-Treatable Aluminum Alloys
Non-heat-treatable aluminum alloys achieve strength through work hardening (or strain hardening) during cold deformation processes (such as cold forging and rolling), rather than through heat treatment to enhance their mechanical properties. The strength of these alloys stems from solid solution strengthening and strain hardening, making them ideal for applications requiring good formability, corrosion resistance, and moderate strength.
· Excellent Corrosion Resistance: Particularly resistant to atmospheric, chemical, and marine corrosion, often outperforming heat-treatable alloys in corrosive environments.
· Good Formability and Workability: Maintain excellent ductility and can be extensively cold worked to achieve higher strength levels through strain hardening.
· Superior Weldability and Joining Characteristics: Generally exhibit better welding performance than heat-treatable alloys, with minimal loss of properties in heat-affected zones.
· Good Electrical and Thermal Conductivity: Maintain high conductivity properties, making them suitable for electrical and thermal management applications.
· Stable Properties at Cryogenic Temperatures: Mechanical properties often improve at low temperatures while maintaining good toughness.
Forged Non-Heat-Treatable Aluminum Components by Simis Aluminum Forging Factory:
Marine and shipbuilding components; chemical processing equipment; electrical busbars and connectors; cryogenic storage tanks; automotive body panels; architectural structures; food processing equipment.
Forged Non-Heat-Treatable Aluminum Alloy Categories used by Simis Aluminum Forging Factory:
· Pure Aluminum and Low-Alloy Forgings
Common Applications: Electrical conductors, heat exchangers, chemical equipment, and decorative applications.
Common Grades: AA 1050 (Al99.5), AA 1060 (Al99.6), AA 1100 (Al99.0Cu)
· Aluminum-Manganese (Al-Mn) Alloy Forgings
Common Applications: Cooking utensils, heat exchangers, storage tanks, and architectural applications.
Common Grades: AA 3003 (AlMn1Cu), AA 3004 (AlMn1Mg1)
· Aluminum-Magnesium (Al-Mg) Alloy Forgings
Common Applications: Marine hardware, boat hull components, pressure vessels, and transportation equipment.
Common Grades: AA 5052 (AlMg2.5), AA 5083 (AlMg4.5Mn0.7), AA 5754 (AlMg3)
· Aluminum-Magnesium-Silicon (Al-Mg-Si) Alloy Forgings
Common Applications: Architectural extrusions, automotive body panels, and general engineering applications.
Common Grades: AA 6061 (AlMg1SiCu), though primarily heat-treatable, some non-heat-treatable variants exist
2. Aluminum-Copper Alloys
Forged aluminum-copper alloys are produced by heating and compression-deforming aluminum-copper alloy billets, followed by solution heat treatment and aging to achieve their optimal mechanical properties. Aluminum-copper alloys are among the strongest aluminum materials, offering an excellent strength-to-weight ratio and good fatigue resistance, making them ideal for high-performance structural applications. However, their corrosion resistance is generally lower than that of other aluminum alloys, and they often require protective coatings or cladding to withstand harsh environments.
· High Strength-to-Weight Ratio: Offer the highest strength levels among aluminum alloys when properly heat-treated, combined with low density.
· Excellent Fatigue Resistance: Good resistance to cyclic loading and vibration, making them suitable for aerospace and automotive applications.
· Good Machinability: Can be machined to precision tolerances and excellent surface finishes in the heat-treated condition.
· Maintain Strength at Elevated Temperatures: Retain mechanical properties better than most other aluminum alloys at temperatures up to 150°C.
· Good Anodizing Response: Can be anodized for improved surface hardness and corrosion resistance.
Forged Aluminum-Copper Components by Simis Aluminum Forging Factory:
Aircraft structural components and fuselage frames; automotive suspension parts and wheels; high-performance sporting goods; robotic arms and machinery parts.
Forged Aluminum-Copper Alloy Categories used by Simis Aluminum Forging Factory:
· Binary Aluminum-Copper Alloy Forgings
Common Applications: General high-strength structural components, automotive parts, and machinery components.
Common Grades: AA 2014 (AlCu4SiMg), AA 2219 (AlCu6Mn)
· Aluminum-Copper with Magnesium Addition Forgings
Common Applications: Aircraft structural members, truck frames, and high-stress components.
Common Grades: AA 2024 (AlCu4Mg1), AA 2017 (AlCu4MgSi)
· Aluminum-Copper with Lithium Addition Forgings
Common Applications: high-performance automotive parts.
Common Grades: AA 2090 (AlCu2Li3), AA 2099 (AlCu2Li1Mg0.5)
· High-Strength Aluminum-Copper Forgings
Common Applications: high-performance racing components.
Common Grades: AA 2618 (AlCu2Mg1.5Ni1), AA 2218 (AlCu4Mg2Ni1)
3. Aluminum-Magnesium-Silicon Alloys
Forged aluminum-magnesium-silicon alloys are manufactured by heating and forming Al-Mg-Si alloy billets through compressive deformation, followed by solution heat treatment and artificial aging to achieve optimal mechanical properties. Aluminum-magnesium-silicon alloys offer an excellent balance of medium-to-high strength, good corrosion resistance, and exceptional extrudability, making them one of the most versatile and widely used aluminum alloy families.
· Good Strength-to-Weight Ratio: Provide medium to high strength levels after heat treatment, combined with low density for weight-sensitive applications.
· Excellent Corrosion Resistance: Demonstrate very good resistance to atmospheric and marine corrosion, superior to most aluminum-copper alloys.
· Good Formability and Weldability: Can be easily formed and welded using various methods while maintaining good mechanical properties.
· Excellent Extrudability: Among the best extrudable aluminum alloys, allowing complex cross-sectional profiles to be produced.
· Good Machinability: Can be machined to precision tolerances and good surface finishes in the heat-treated condition.
Forged Aluminum-Magnesium-Silicon Components by Simis Aluminum Forging Factory:
Automotive chassis components and body structures; bicycle frames and components; architectural extrusions and structures; heat exchanger components; marine fittings and hardware; electrical conductor components; general engineering structural parts.
Forged Aluminum-Magnesium-Silicon Alloy Categories used by Simis Aluminum Forging Factory:
· Balanced Mg₂Si Alloy Forgings
Common Applications: General structural components, automotive parts, and architectural applications.
Common Grades: AA 6061 (AlMg1SiCu), AA 6063 (AlMg0.7Si)
· High-Silicon Alloy Forgings
Common Applications: High-strength structural components, wear-resistant parts, and automotive suspension components.
Common Grades: AA 6082 (AlMg1SiMn), AA 6005 (AlMg0.8Si)
· High-Magnesium Alloy Forgings
Common Applications: Marine structures, pressure vessels, and transportation equipment components.
Common Grades: AA 6101 (AlMg0.6Si), AA 6151 (AlMg1SiCr)
· Copper-Containing Alloy Forgings
Common Applications: High-strength structural components, aerospace parts, and precision machinery components.
Common Grades: AA 6061 (AlMg1SiCu), AA 6013 (AlMg1SiCuMn)
4. Aluminum-Zinc Alloys
Forged aluminum-zinc alloys are produced by heating and compression-deforming aluminum-zinc alloy billets. They utilize their natural aging properties to achieve high strength without the need for solution heat treatment, making them cost-effective for a variety of structural applications. They are particularly well-suited for applications requiring high strength without complex heat treatment processes.
· High As-Cast Strength: Achieve high mechanical properties in the as-cast condition through natural aging, reducing heat treatment requirements.
· Good Machinability: Can be machined to precision tolerances with good chip formation and surface finish characteristics.
· Excellent Casting Characteristics: Demonstrate good fluidity and feeding characteristics during the casting process.
· Natural Aging Properties: Continue to strengthen naturally at room temperature after solidification.
· Good Corrosion Resistance: Provide adequate resistance to general atmospheric corrosion for most applications.
Forged Aluminum-Zinc Components by Simis Aluminum Forging Factory:
Automotive engine brackets and mounts; structural hardware components; machinery parts and fittings; electrical hardware; general engineering components; architectural fittings.
Forged Aluminum-Zinc Alloy Categories used by Simis Aluminum Forging Factory:
· High-Zinc Aluminum Alloy Forgings
Common Applications: Automotive structural components, high-strength machinery parts, and structural fittings.
Common Grades: AA 7075 (AlZn5.5MgCu), AA 7005 (AlZn4.5Mg1.5Mn)
· Zinc-Magnesium Alloy Forgings
Common Applications: General structural components, marine hardware, and transportation equipment parts.
Common Grades: AA 7108 (AlZn5.5Mg1.5), AA 7003 (AlZn6Mg0.8Zr)
· Zinc-Copper Alloy Forgings
Common Applications: High-strength structural components, aerospace parts, and precision machinery components.
Common Grades: AA 7175 (AlZn5.5MgCu1.5), AA 7475 (AlZn5.5MgCu2)
· Low-Zinc Alloy Forgings
Common Applications: Marine components, architectural structures, and general engineering applications.
Common Grades: AA 7010 (AlZn6MgCu), AA 7020 (AlZn4.5Mg1)
Application of Aluminum Forgings
Custom Aluminum Forgings by Simis Forging Factory
Aluminum Forging Company's Custom Steps
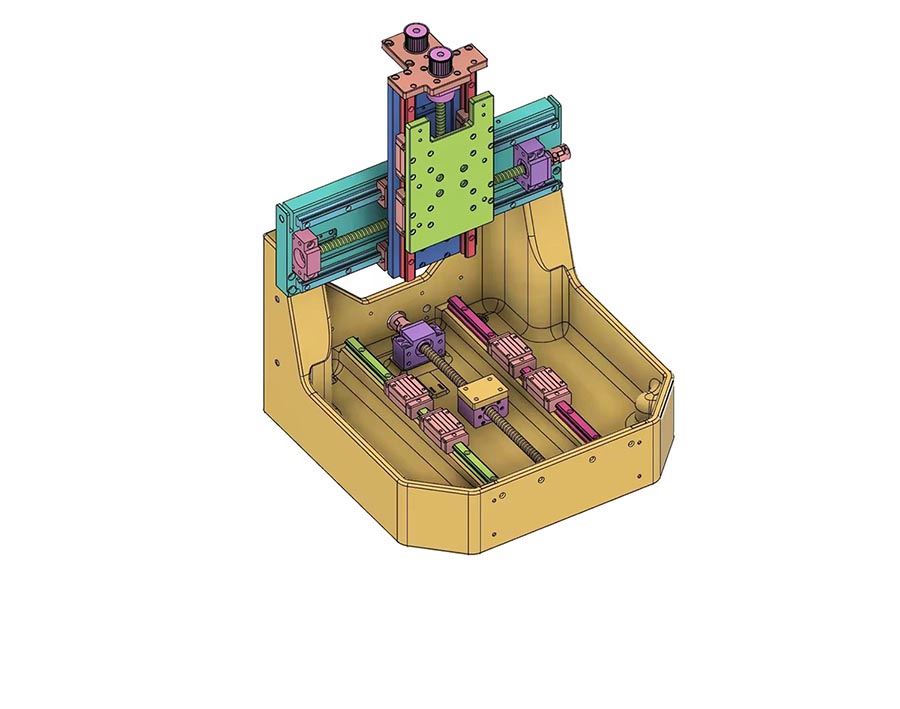
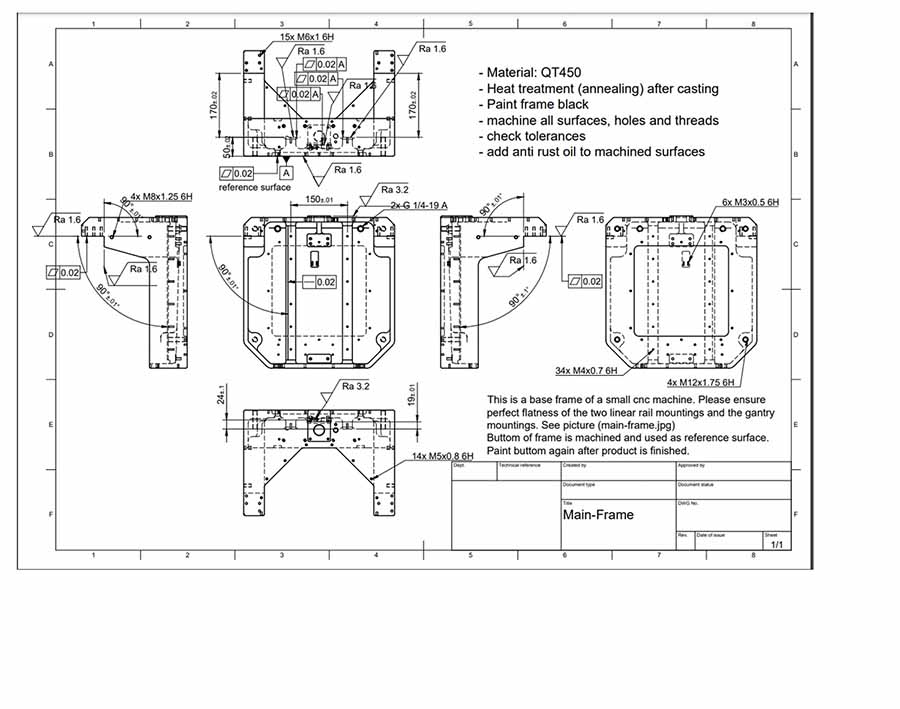

Confirm customization requirements
1. Provide detailed design documents or samples of parts
The Simis engineering team will analyze the 3D drawings (CAD models) and processing drawings of forgings provided by customers to ensure that they meet the manufacturing requirements.
Samples: If customers can provide samples, we can also forge and replicate them according to the samples.
2. Confirm the performance requirements of aluminum forgings
Clearly define the various performance requirements of forgings, such as strength, hardness, wear resistance, corrosion resistance, etc., and confirm the surface roughness, appearance quality, dimensional tolerance and accuracy requirements of aluminum alloy forgings.
3. Confirm the aluminum alloy forging material
Select the appropriate forging material according to the use environment, technical requirements or customer requirements of the parts. Simis will give reasonable suggestions based on the price, mechanical properties, wear resistance, corrosion resistance, etc. of the material.
4. Confirm the aluminum alloy forging process
Determine the appropriate forging process based on the price, shape, size, accuracy, material, etc. of the parts.
5. Make samples
Forge the selected forging materials through the corresponding process to produce the first batch of samples.
6. Comprehensive inspection of samples
The produced samples will be fully inspected to ensure that they meet the design standards and customer quality requirements.
Dimension and tolerance inspection, performance testing, chemical composition analysis, non-destructive testing and other test reports
Production and quality control
7. Mass production
After the sample is confirmed and approved by the customer, the mass production schedule is arranged according to the order requirements, and the production materials are prepared. The same aluminum forging equipment and process as the sample stage are used in the mass production process.
8. Mass production quality control
We implement strict quality control measures during the production process to ensure that the quality of each aluminum alloy forgings in mass production meets customer requirements. During the production process, the size, appearance, physical properties, etc. of the aluminum forgings are regularly inspected to ensure the consistency of each batch of parts.
9. Post-production product quality inspection
Multiple inspections by multiple people: We will arrange different inspectors to conduct multiple random inspections on the final product, including dimensional accuracy, surface quality, strength, hardness, etc., to ensure that the aluminum parts produced meet customer requirements.
10. Parts packaging and delivery
Packaging: Pack and ship the parts that have passed the quality inspection, and select the appropriate packaging method and the appropriate logistics method (such as air, sea, and land transportation) to deliver them to customers on time.




If you want to custom parts, please send me the design drawings and 3D drawings of theparts you want to customize by email, and we will calculate an accurate price for you bylooking at the detailed part parameters and 3D model.





















